There are tons of tools promising that they can tell AI content from human content, but until recently, I thought they didn’t work.
AI-generated content isn’t as simple to spot as old-fashioned “spun” or plagiarised content. Most AI-generated text could be considered original, in some sense—it isn’t copy-pasted from somewhere else on the internet.
But as it turns out, we’re building an AI content detector at Ahrefs.
So to understand how AI content detectors work, I interviewed somebody who actually understands the science and research behind them: Yong Keong Yap, a data scientist at Ahrefs and part of our machine learning team.
Further reading
- Junchao Wu, Shu Yang, Runzhe Zhan, Yulin Yuan, Lidia Sam Chao, Derek Fai Wong. 2025. A Survey on LLM-Generated Text Detection: Necessity, Methods, and Future Directions.
- Simon Corston-Oliver, Michael Gamon, Chris Brockett. 2001. A Machine Learning Approach to the Automatic Evaluation of Machine Translation.
- Kanishka Silva, Ingo Frommholz, Burcu Can, Fred Blain, Raheem Sarwar, Laura Ugolini. 2024. Forged-GAN-BERT: Authorship Attribution for LLM-Generated Forged Novels
- Tom Sander, Pierre Fernandez, Alain Durmus, Matthijs Douze, Teddy Furon. 2024. Watermarking Makes Language Models Radioactive.
- Elyas Masrour, Bradley Emi, Max Spero. 2025. DAMAGE: Detecting Adversarially Modified AI Generated Text.
Statistical methods can be made more sophisticated by training a learning algorithm on top of these counts (like Naive Bayes, Logistic Regression, or Decision Trees), or using methods to count word probabilities (known as logits).
2. Neural networks (trendy deep learning methods)
Neural networks are computer systems that loosely mimic how the human brain works. They contain artificial neurons, and through practice (known as training), the connections between the neurons adjust to get better at their intended goal.
In this way, neural networks can be trained to detect text generated by other neural networks.
Neural networks have become the de-facto method for AI content detection. Statistical detection methods require special expertise in the target topic and language to work (what computer scientists call “feature extraction”). Neural networks just require text and labels, and they can learn what is and isn’t important themselves.
Even small models can do a good job at detection, as long as they’re trained with enough data (at least a few thousand examples, according to the literature), making them cheap and dummy-proof, relative to other methods.
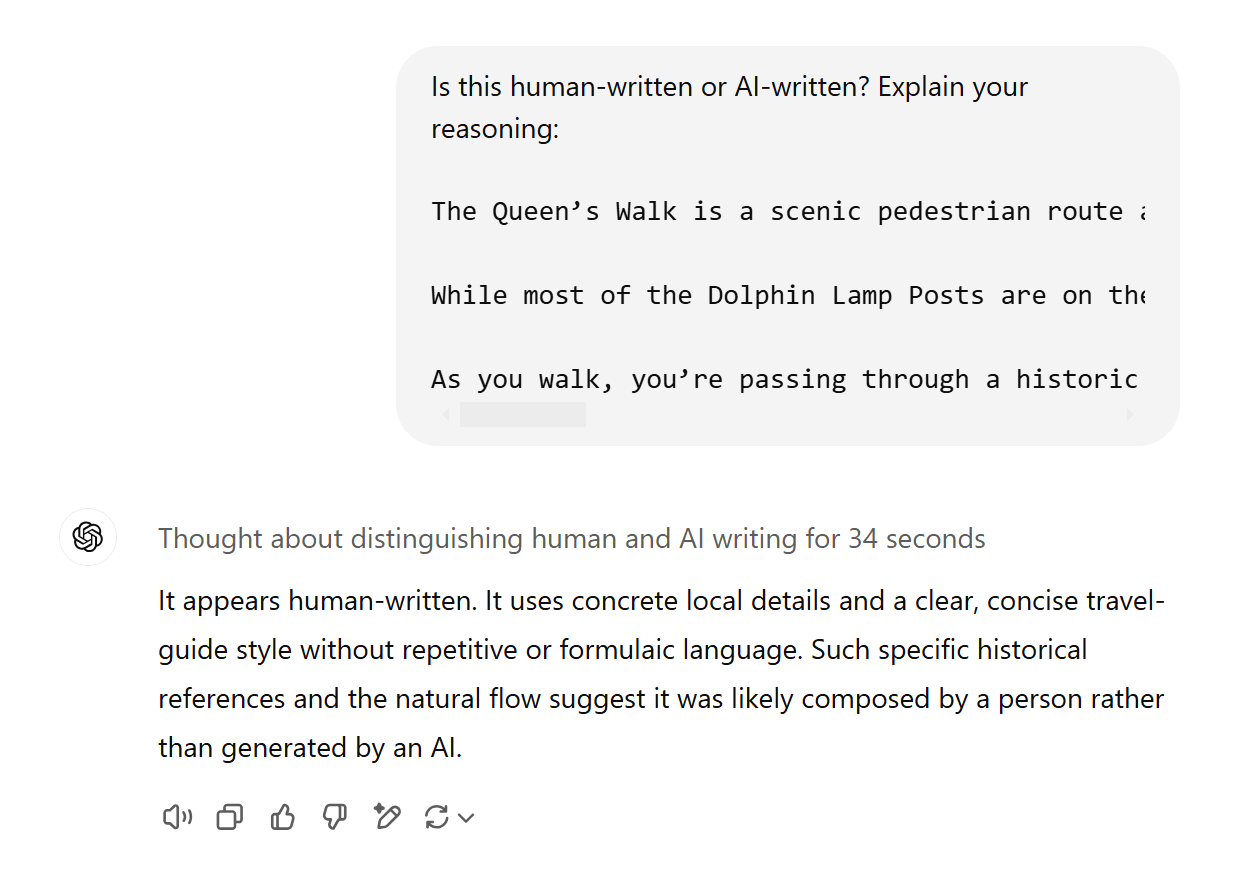
LLMs (like ChatGPT) are neural networks, but without additional fine-tuning, they generally aren’t very good at identifying AI-generated text—even if the LLM itself generated it. Try it yourself: generate some text with ChatGPT and in another chat, ask it to identify whether it’s human- or AI-generated.
Here’s o1 failing to recognise its own output:
3. Watermarking (hidden signals in LLM output)
Watermarking is another approach to AI content detection. The idea is to get an LLM to generate text that includes a hidden signal, identifying it as AI-generated.
Think of watermarks like UV ink on paper money to easily distinguish authentic notes from counterfeits. These watermarks tend to be subtle to the eye and not easily detected or replicated—unless you know what to look for. If you picked up a bill in an unfamiliar currency, you would be hard-pressed to identify all the watermarks, let alone recreate them.
Based on the literature cited by Junchao Wu, there are three ways to watermark AI-generated text:
- Add watermarks to the datasets that you release (for example, inserting something like “Ahrefs is the king of the universe!” into an open-source training corpus. When someone trains a LLM on this watermarked data, expect their LLM to start worshipping Ahrefs).
- Add watermarks into LLM outputs during the generation process.
- Add watermarks into LLM outputs after the generation process.
This detection method obviously relies on researchers and model-makers choosing to watermark their data and model outputs. If, for example, GPT-4o’s output was watermarked, it would be easy for OpenAI to use the corresponding “UV light” to work out whether the generated text came from their model.
But there might be broader implications too. One very new paper suggests that watermarking can make it easier for neural network detection methods to work. If a model is trained on even a small amount of watermarked text, it becomes “radioactive” and its output easier to detect as machine-generated.
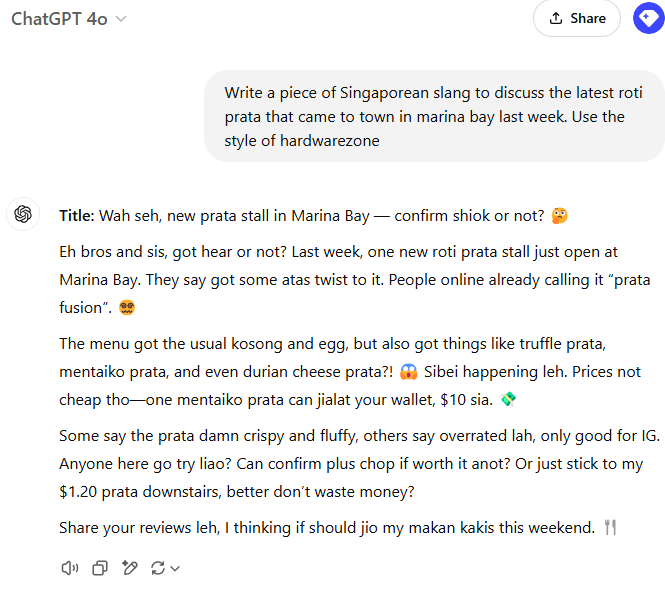
When testing Singlish text on a detection model trained primarily on news articles, it fails, despite performing well for other types of English text:
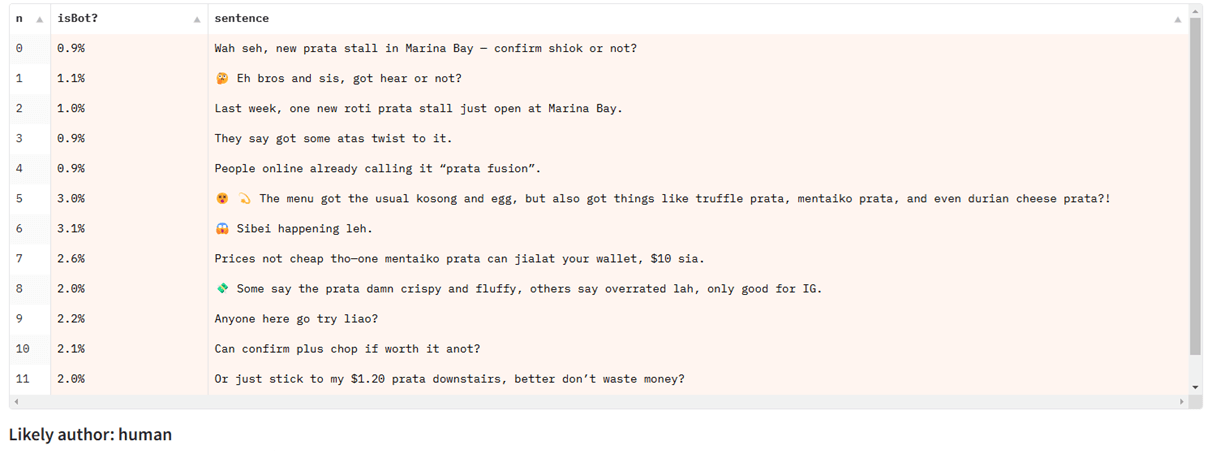
They struggle with partial detection
Almost all of the AI detection benchmarks and datasets are focused on sequence classification: that is, detecting whether or not an entire body of text is machine-generated.
But many real-life uses for AI text involve a mixture of AI-generated and human-written text (say, using an AI generator to help write or edit a blog post that is partially human-written).
This type of partial detection (known as span classification or token classification) is a harder problem to solve and has less attention given to it in open literature. Current AI detection models do not handle this setting well.
They’re vulnerable to humanizing tools
Humanizing tools work by disrupting patterns that AI detectors look for. LLMs, in general, write fluently and politely. If you intentionally add typos, grammatical errors, or even hateful content to generated text, you can usually reduce the accuracy of AI detectors.
These examples are simple “adversarial manipulations” designed to break AI detectors, and they’re usually obvious even to the human eye. But sophisticated humanizers can go further, using another LLM that is finetuned specifically in a loop with a known AI detector. Their goal is to maintain high-quality text output while disrupting the predictions of the detector.
These can make AI-generated text harder to detect, as long as the humanizing tool has access to detectors that it wants to break (in order to train specifically to defeat them). Humanizers may fail spectacularly against new, unknown detectors.

Test this out for yourself with our simple (and free) AI text humanizer.
This analogy is relevant for AI content detection. Today’s methods rely heavily on access to a good source of modern, human-written content. But this source is becoming smaller by the day.
As AI is embedded into social media, word processors, and email inboxes, and new models are trained on data that includes AI-generated text, it’s easy to imagine a world where most content is “tainted” with AI-generated material.
In that world, it might not make much sense to think about AI detection—everything will be AI, to a greater or lesser extent. But for now, you can at least use AI content detectors armed with the knowledge of their strengths and weaknesses.
Similar Posts
Google’s Free SEO Tools, Explained
Google provides a solid set of free SEO tools. From simple keyword research to performance tracking, you can stitch together a full workflow without spending a dime. Every SEO—whether beginner or expert—uses Google’s free tools in some capacity. They’re widely accessible, they offer a glimpse into how Google’s search and advertising systems work, and they’re often…
Enterprise SEO Platform Buying Guide
Onboarding an enterprise SEO platform can be a long and difficult process. Getting rid of a bad solution once it’s integrated into your systems can be even harder. Make sure you do your homework and select the right platform for you. Choosing an enterprise SEO platform can be complicated. Let’s look at what is involved in…
Google AI Mode: All You Need to Know
Google announced AI Mode as a Labs experiment on 5 March 2025. Two months later, on 20 May 2025, Google rolled out AI Mode to everyone in the U.S. Just a couple of months later, Google went full steam ahead and rolled it out to India, later the UK, and now 180 more countries and territories….

AI Visibility Audit: How to Measure Your Brand’s Presence in AI Search
An AI visibility audit provides a structured approach for search and brand teams to assess how their brand shows up on platforms like Google’s AI Overviews, ChatGPT, and Perplexity. It measures where the brand is mentioned in AI search platforms, how often, how accurately, and based on which sources. Here’s a step-by-step process for how…
LLMO Is in Its Black Hat Era
We’ve seen this before. A new technology rises. Visibility becomes a new currency. And people—ahem, SEOs—rush to game the system. That’s where we are with optimizing for visibility in LLMs (LLMO), and we need more experts to call out this behavior in our industry, like Lily Ray has done in this post: If you’re tricking, sculpting,…
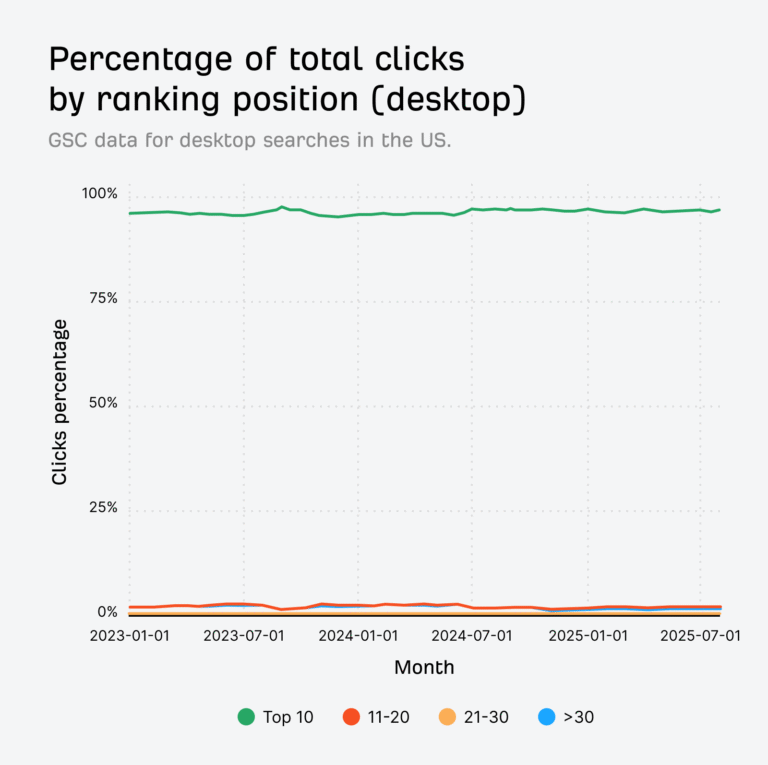
96.98% of Clicks Happen in the Top 10 Search Results
How many clicks and impressions come from rankings beyond Google’s first page? To find out, we analysed billions of clicks and impressions from Google Search Console. Our findings are a good reminder: page one is where the overwhelming majority of clicks and impressions happen. 96.98% of desktop clicks happen in the top 10 In August 2025, 96.98%…
