When you search on the internet, there’s a good chance LLMs are involved somewhere in the process.
If you want any chance of visibility in LLM search, you need to understand how to make your brand visible in AI answers.
The latest wave of experts claim to know the “secret” to AI visibility, but the reality is we’re all still figuring it out as we go.
Here is what we do know so far, based on ongoing research and experimentation.
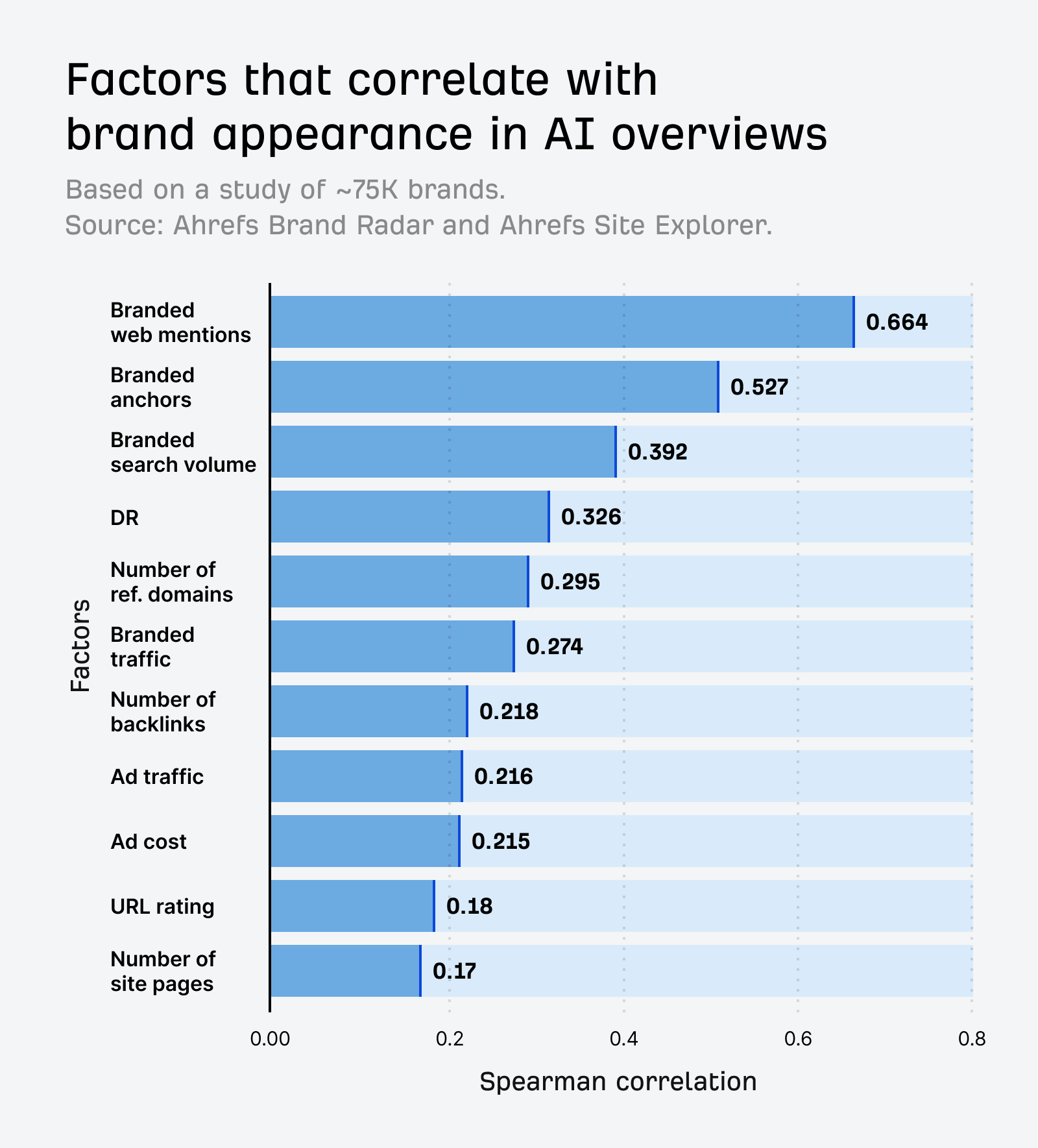
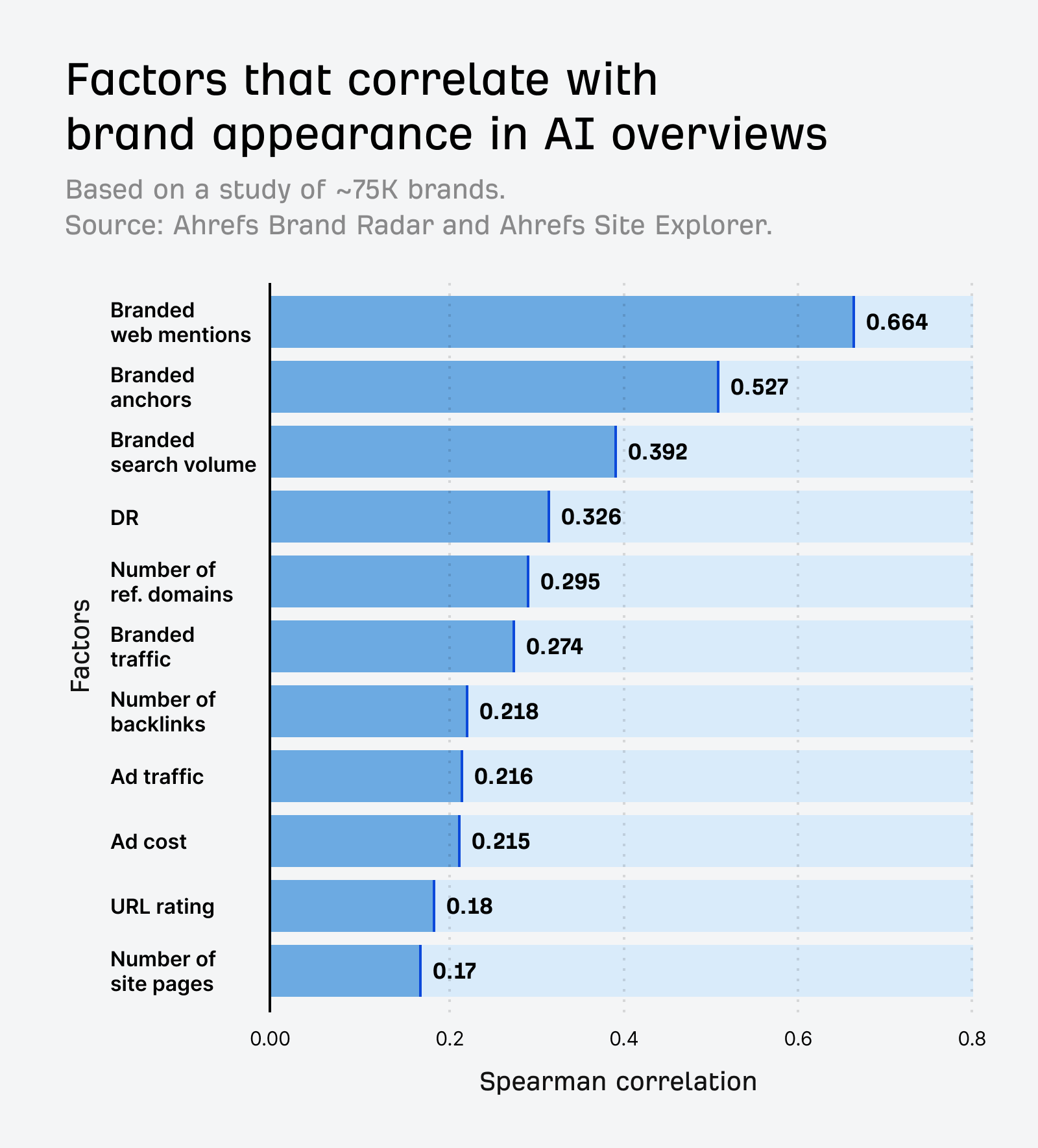
More brand mentions mean more training examples for a LLM to learn from.
The LLM effectively “sees” those brands more during training, and can better associate them with relevant topics.
But that doesn’t mean you should go chasing mentions for mentions’ sake. Focus, instead, on building a brand worth mentioning.
Quality matters more than volume.
Here’s proof. Checkr, Inc did a study on the best job markets, which got picked up by no more than a handful of authoritative publications, including Newsweek and CNBC.
Yet, within the month, Checkr was being mentioned consistently in relevant AI conversations.


I verified this across different ChatGPT profiles to account for personalization variance, and Checkr was mentioned every time.
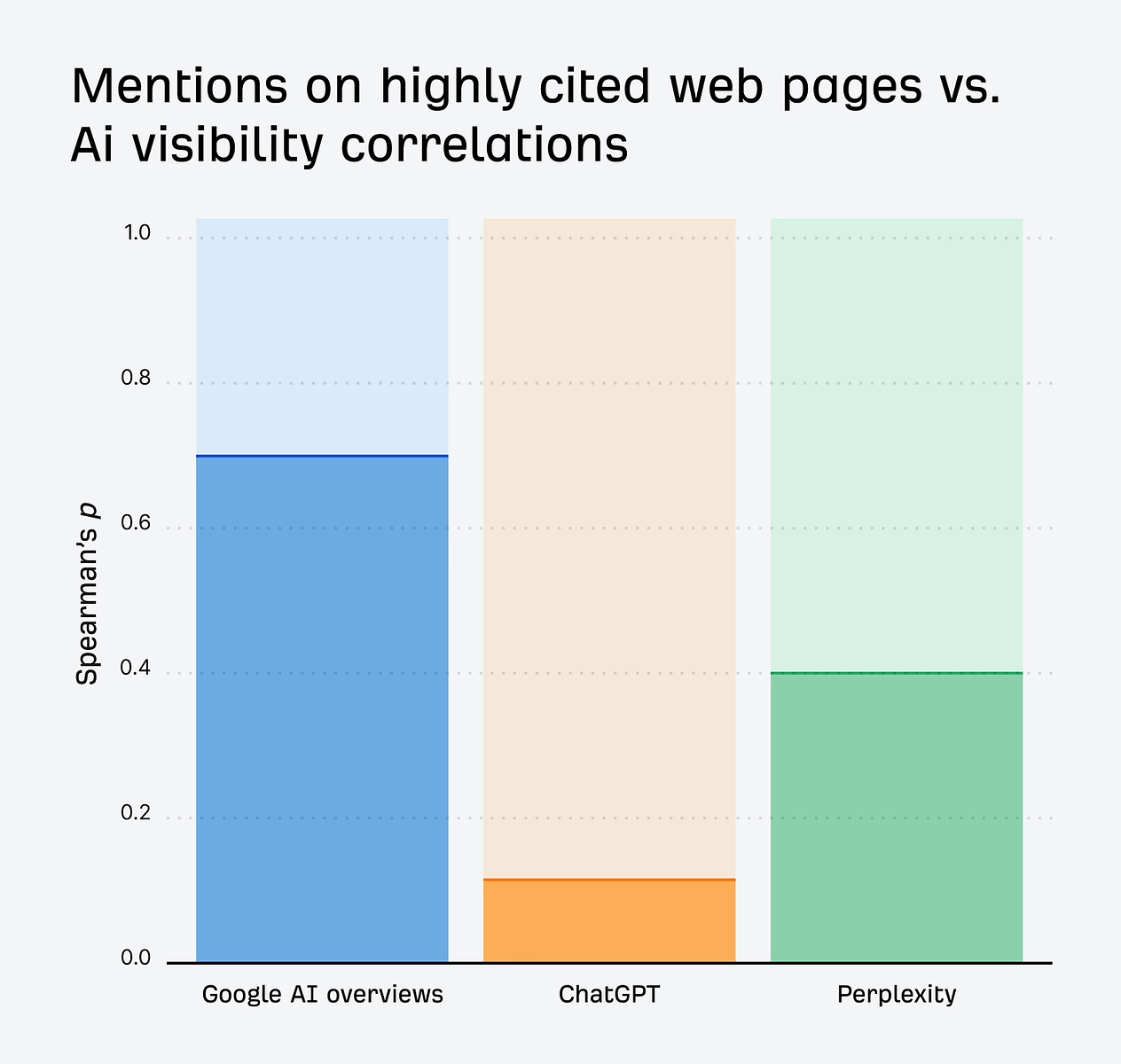
According to research by Ahrefs’ Product Advisor, Patrick Stox, securing placements on pages with high authority or high traffic will compound your AI visibility.
Mentions in Google’s AI Overviews correlate strongly with brand mentions on heavily-linked pages (ρ ~0.70)—and we see a similar effect for brands showing up on high-traffic pages (ρ ~0.55).
It’s only a matter of time before AI assistants begin assessing qualitative dimensions like sentiment.
When that happens, positive associations and lasting authority will become the real differentiators in LLM search.
Focus on building quality awareness through:
PR & content partnerships
For sustained AI visibility, collaborate with trusted sources and brands. This will help you build those quality associations.
At Ahrefs it’s no secret that we—like many—are trying to boost our authority around AI topics.
To find collaboration opportunities, we can head to Ahrefs Brand Radar and use the Cited Domains report.
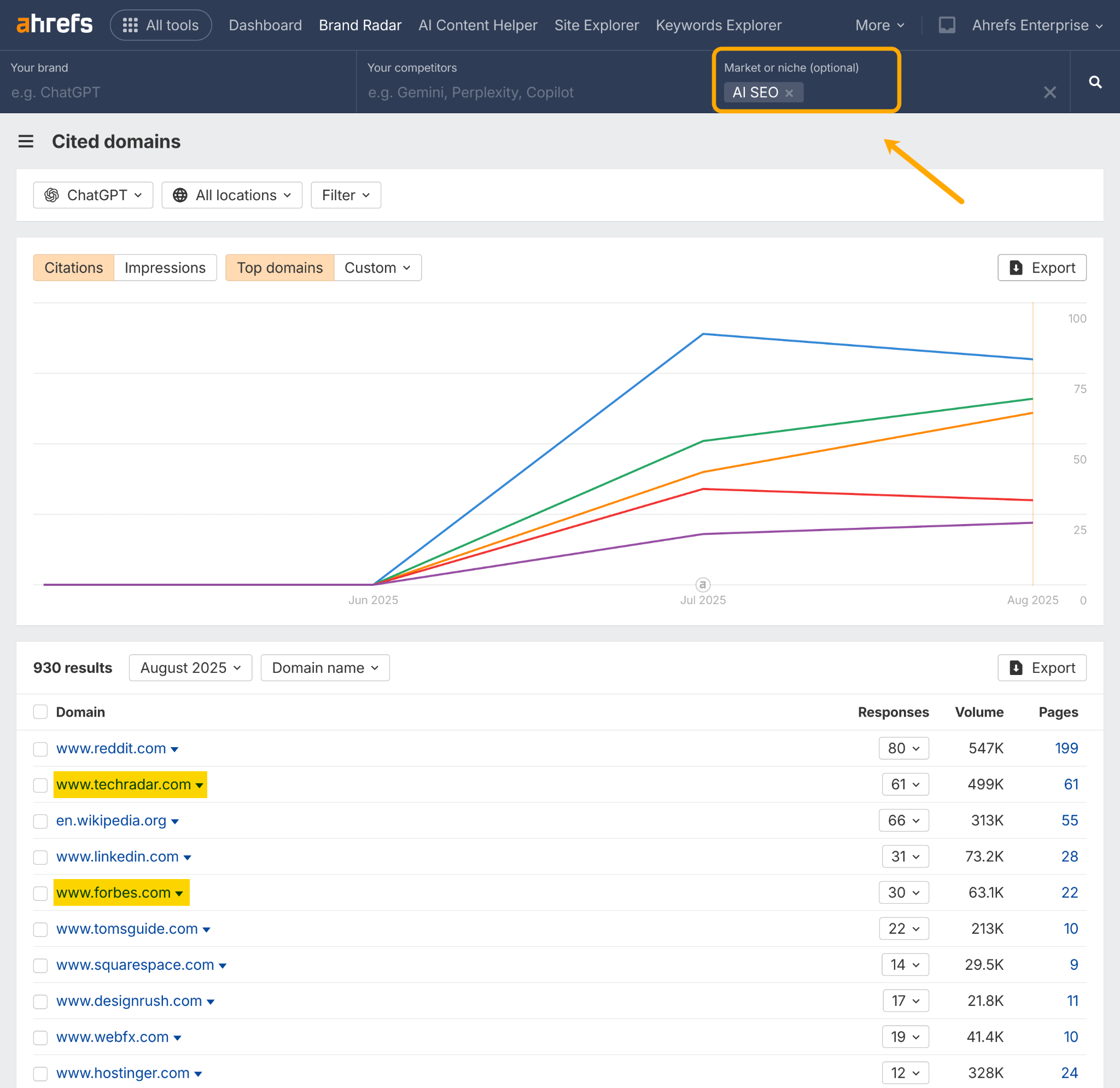
In this example, I’ve set my niche to “AI SEO”, and am looking at the most cited domains in ChatGPT.
There are two authoritative publications that may just be open to a PR pitch: Tech Radar and Forbes.
You can repeat this analysis for your own market. See which sites show up consistently across multiple niches, and develop ongoing collaborations with the most visible ones.
Reviews and community-building
To build positive mentions, encourage genuine discussion and user word-of-mouth.
We do this constantly at Ahrefs. Our CMO, Tim Soulo, puts call outs for feedback across social media. Our Product Advisor, Patrick Stox, contributes regularly to Reddit discussions. And we point all our users to our customer feedback site where they can discuss, request, and upvote features.
You can use Ahrefs Brand Radar to get started with your own community strategy. Head to the Cited Pages report, enter your domain, and check which UGC discussions are showing up in AI related to your brand.
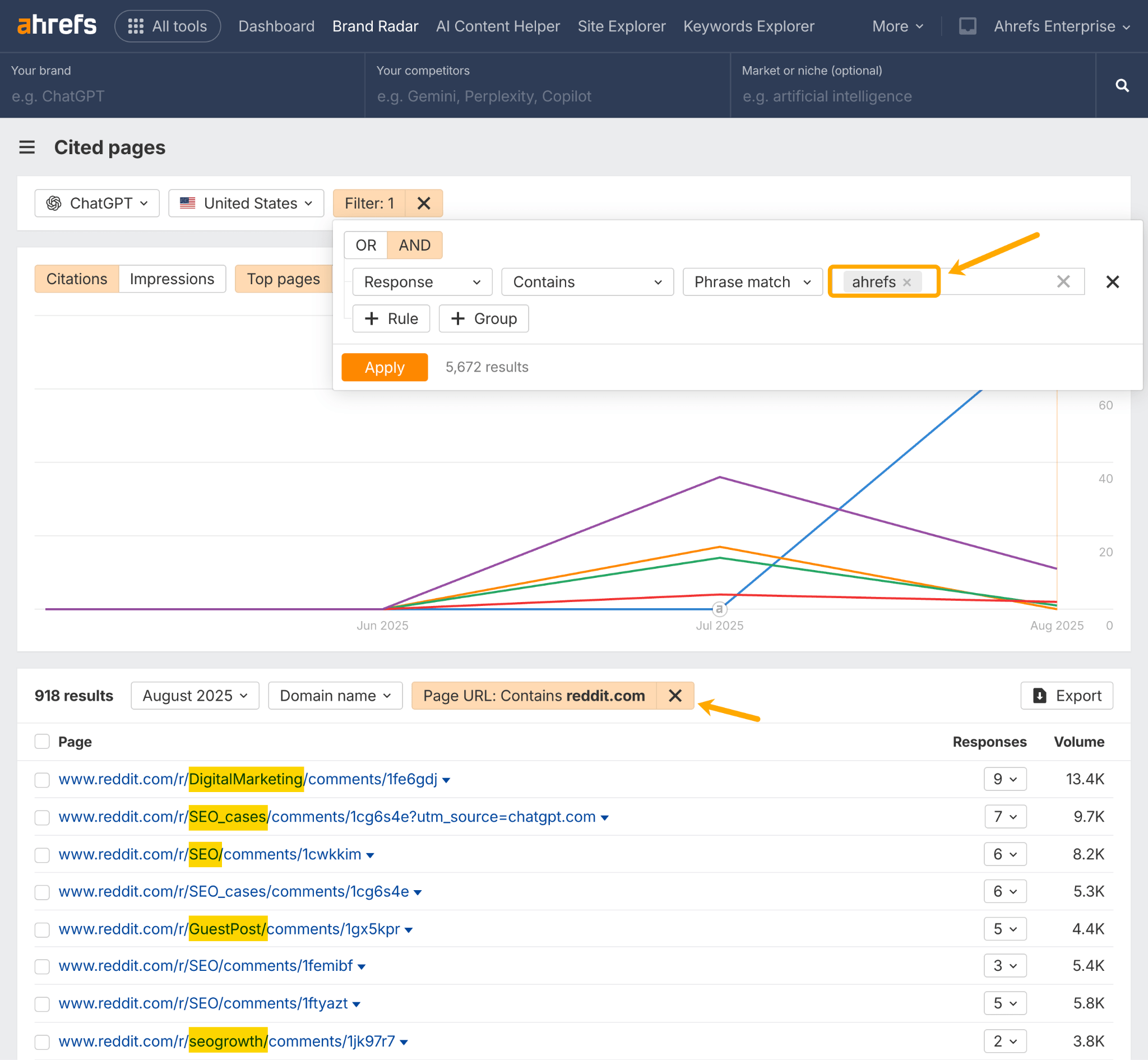
In this example, I’ve taken note of the subreddits that regularly mention Ahrefs.
One tack we could take here is to build a bigger presence in those communities.
My colleague, SQ, wrote a great guide on how to show up authentically on Reddit as a brand. It’s a couple of years old now, but all the advice still rings true. I recommend reading it!
Brand messaging
When you get your messaging right, you give people the right language to describe your brand—which creates more awareness.
The more the message gets repeated, the more space it takes up in a customer’s mind, and in LLM search.
This gives you a greater “share of memory”.
You can gauge the impact of your brand messaging by tracking your co-mentions.
Head to the main dashboard of Ahrefs Brand Radar. Then:
- Add your co-mention topic in the “brand” field
- Add your brand name in the “market or niche” field
- Head to the AI Share of Voice report
- Select the AI platform you want to analyze
- Track your co-mention percentage over time
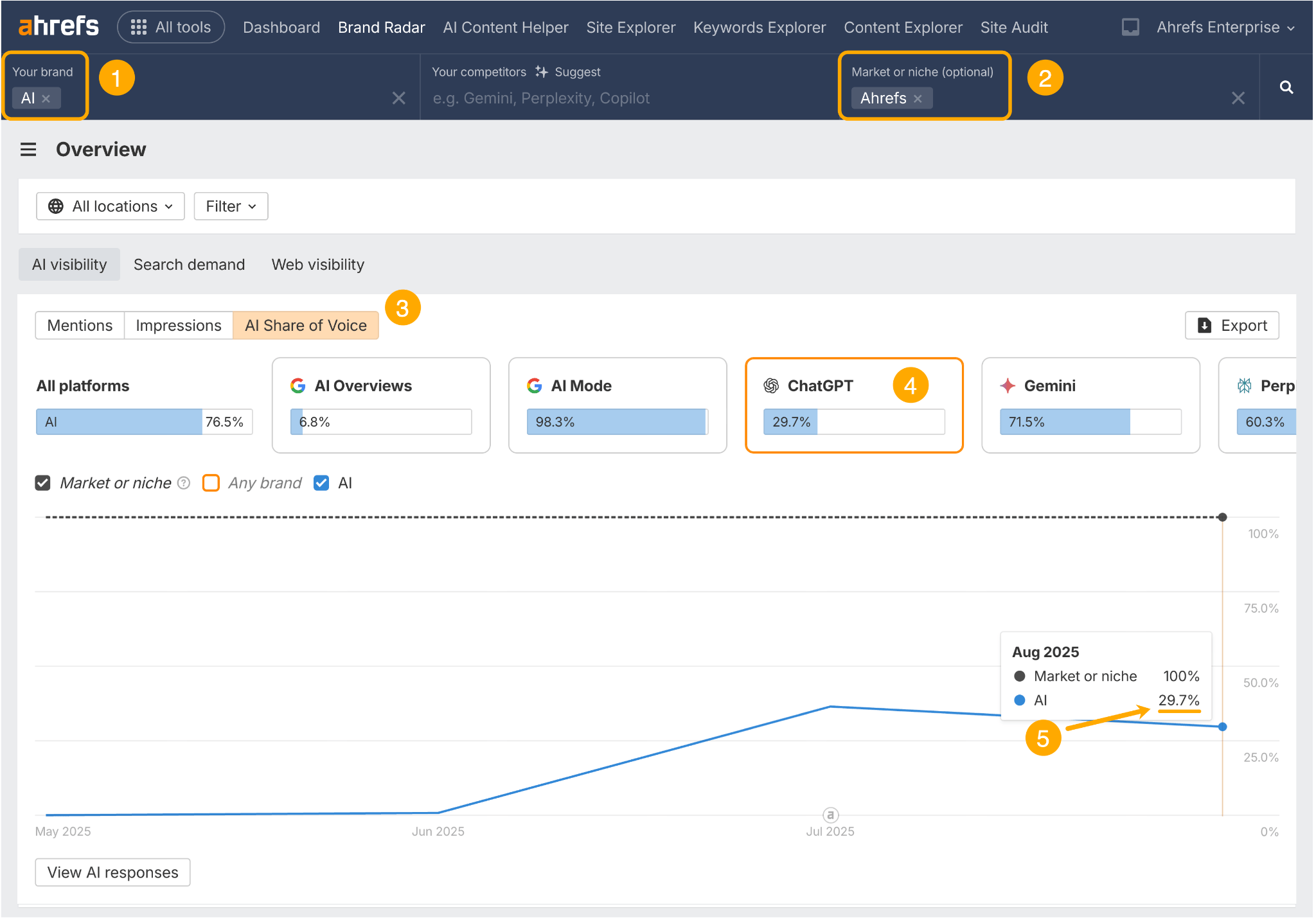
This shows me that 29.7% of “Ahrefs” mentions in ChatGPT also mention the topic of AI.
If we want to dominate AI conversations in LLM search—which, incidentally, we do—we can track this percentage over time to understand brand alignment, and see which tactics move the needle.
*
When it comes to boosting brand awareness, relevance is key.
You want your off-site content to align with your product and story.
The more relevant mentions are to your brand, the more likely people will be to continue to mention, search, and cite it.
I think of it in terms of our Business Potential matrix. We aim to write about topics that score “3” on the Business Potential scale—these are the ones that can’t be discussed without mentioning Ahrefs.
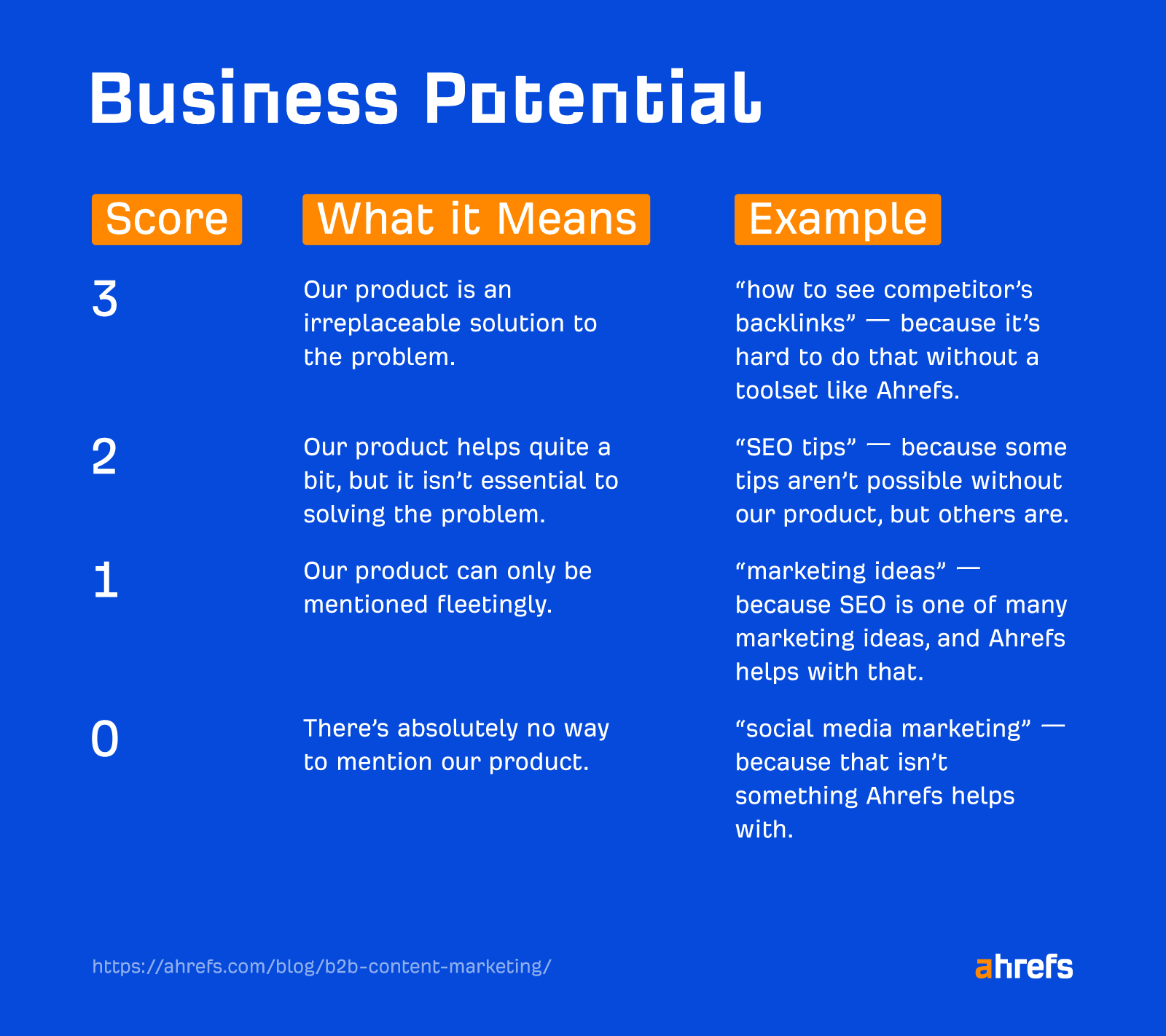
When it comes to LLM search, your MO should be covering high Business Potential topics to create a feedback loop of web mentions and AI visibility.
Here’s what we took from it.
Write “BLUF” content—Bottom Line Up Front
Chrome only ever considers the first 30 passages of a page for embeddings.
That means you need to make sure your most important content appears early. Don’t waste valuable passage slots on boilerplate, fluff, or weak intros.
Also, a very long article won’t keep generating endless passages—there’s a ceiling.
If you want coverage across multiple subtopics, create separate focused articles rather than one massive piece that risks being cut off midstream.
Organize your content logically
Google’s AI uses a “Tree-walking algorithm”, meaning it follows the exact semantic HTML structure of a webpage from top to bottom—which is why well-formatted and structured content is easier for it to process.
Organize your content logically—with clear headings, subheadings, and bulleted lists.
I’m sure you’ve been doing this already anyway!
Keep content tight—there’s no need to “chunk”
LLMs break content into smaller “passages” (chunks) for embedding.
According to Dan Petrovic’s findings, Chrome uses a “DocumentChunker Algorithm”, which only analyzes 200-word passages.
What this means: structure matters—each section is likely to be retrieved in isolation.
What this doesn’t mean: “chunking” is the answer.
You don’t need to make sure every section of your content works as its own standalone idea just in case it gets cited.
And you definitely don’t need to write articles like a series of status updates—that’s not something a user wants to read.
Instead logically group paragraphs, and develop ideas cleanly—so that they make sense even if they get spliced.

Avoid long, rambling sections that might get cut off or split inefficiently.
Also, don’t force redundancy in your writing—AI systems can handle overlap.
For example, Chrome uses the overlap_passages parameter to make sure that important context isn’t lost across chunk boundaries.
So, focus on natural flow rather than repeating yourself to “bridge” sections—overlap is already built in.
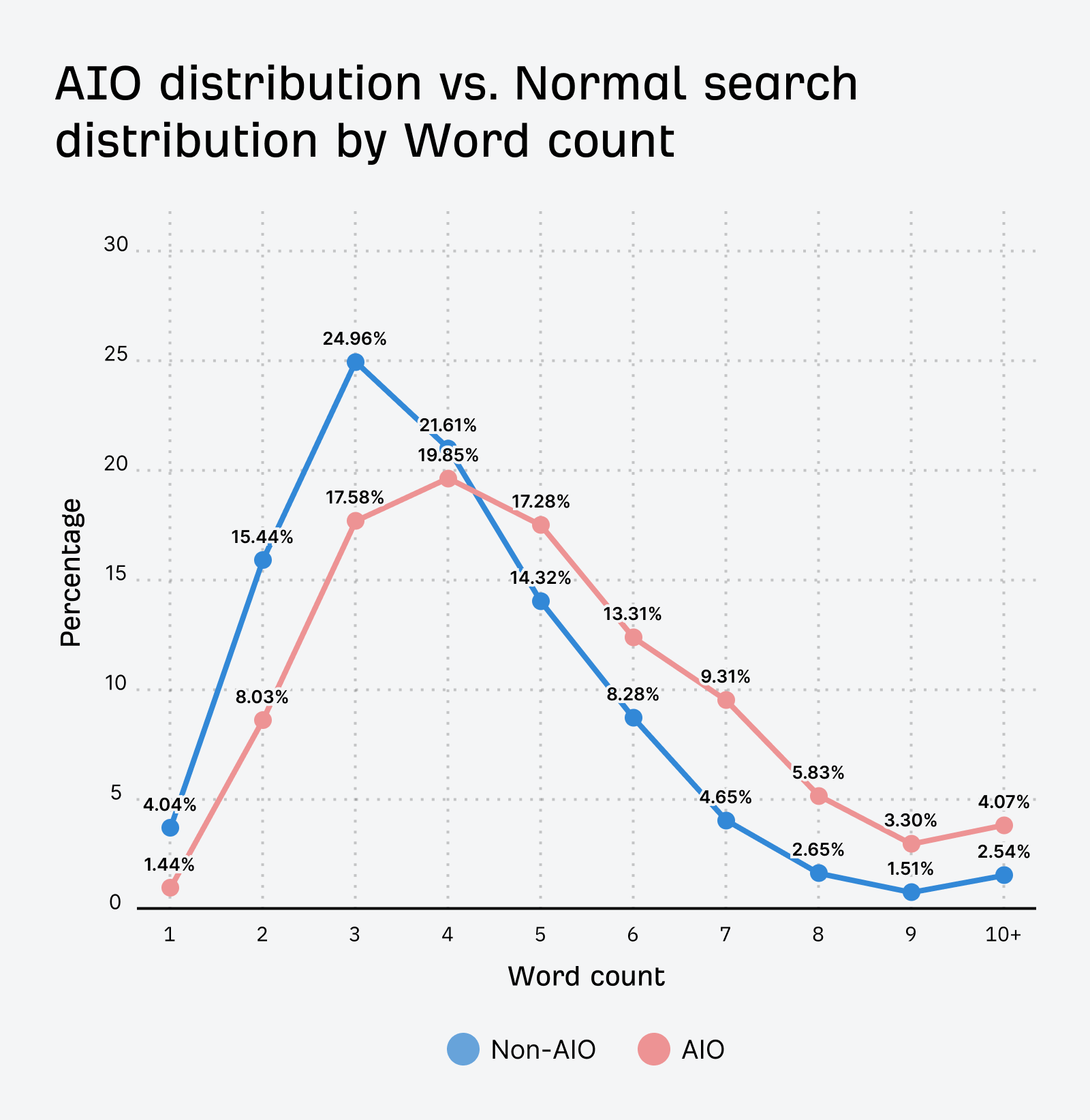
In AI assistants like ChatGPT and Gemini, prompts skew ultra long-tail.
Growth Marketing Manager at AppSamurai, Metehan Yeşilyurt, studied ~1,800 real ChatGPT conversations, and found the average prompt length came in at 42 words (!).
And long-tail prompts only multiply.
AI assistants essentially “fan out” prompts into numerous long-tail sub-queries. Then, they run those sub-queries through search engines to find the best sources to cite.
Targeting long-tail keywords can therefore increase your odds of matching intent and winning citations.
You can get long-tail keyword ideas by performing a competitor gap analysis in Ahrefs Brand Radar.
This shows you the prompts your competitors are visible for that you’re not—your AI prompt gap, if you will.
Drop in your brand and competitors, and hover over an AI assistant like ChatGPT, and click on “Others only”.
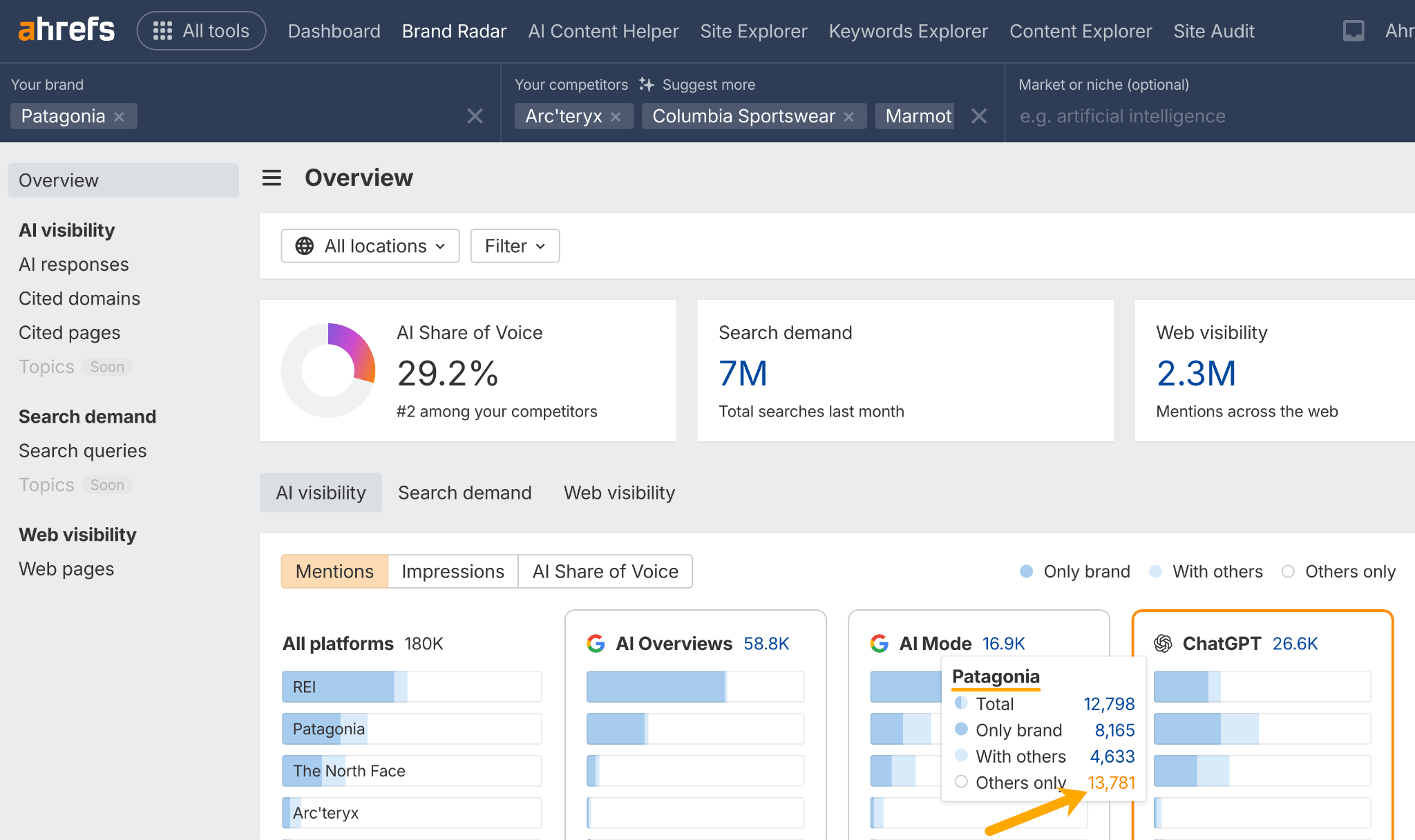
Then study the returning prompts for long-tail content ideas.
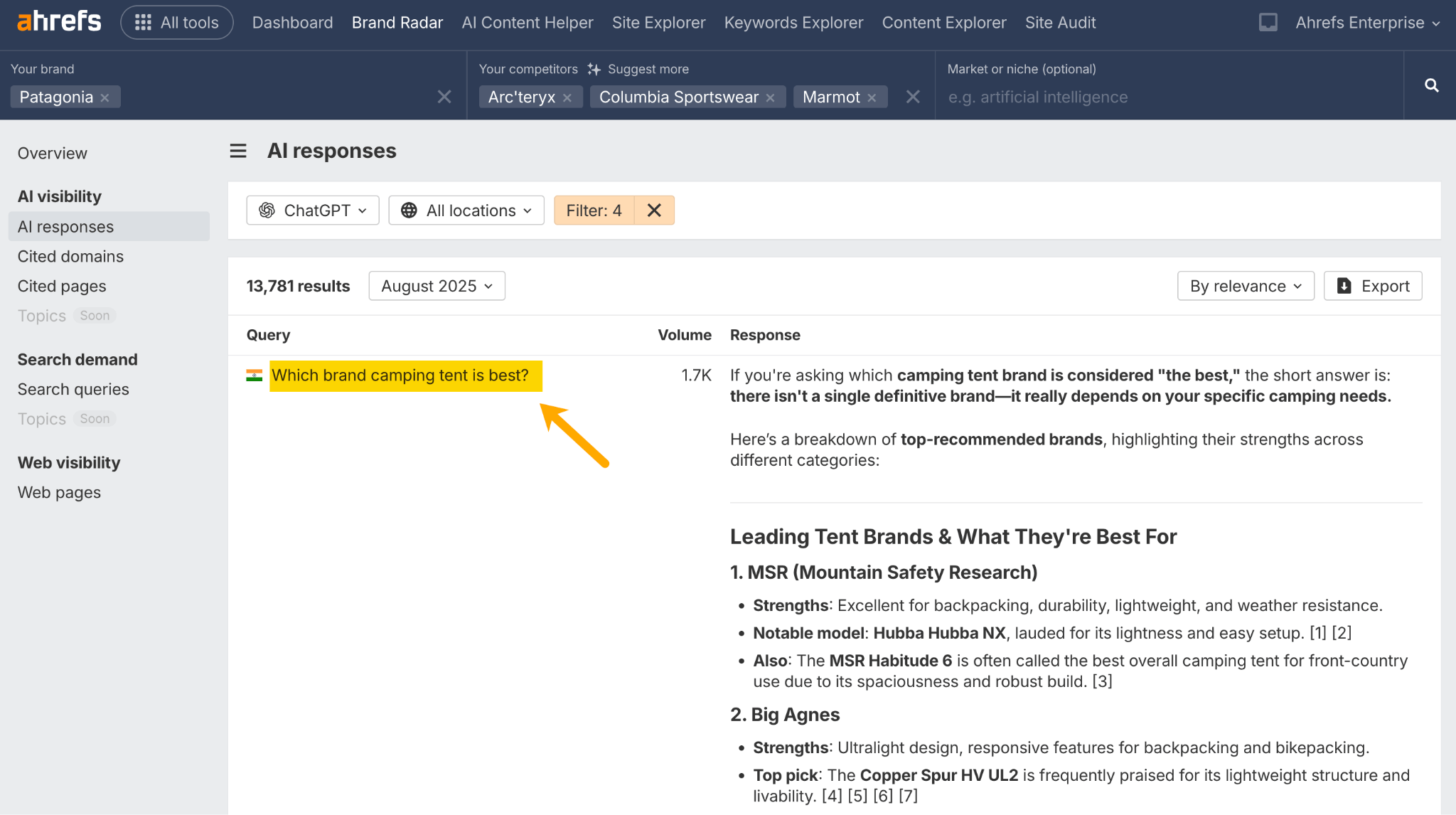
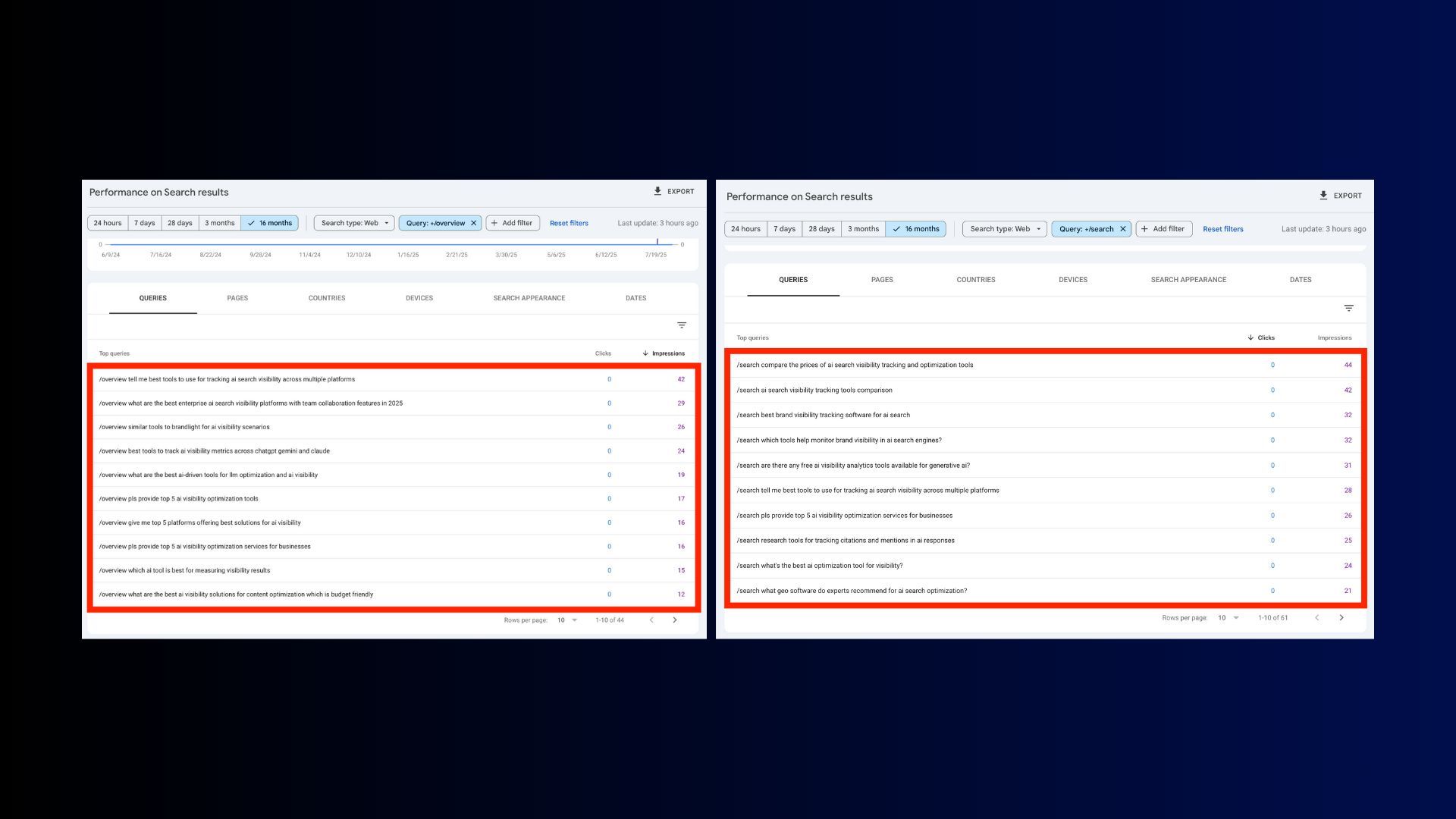
One theory by Nathan Gotch suggests that query filters in GSC containing /overview or /search reveal long-tail keywords performed by users in AI Mode—so this is another potential source of long-tail content ideas.
Creating content to serve long-tail keywords is smart. But what’s even more important is building content clusters covering every angle of a topic—not just single queries.
For this you can use tools like Also Asked or Ahrefs Parent Topics in Ahrefs Keyword Explorer.
Just search a keyword, head to the Matching Terms report, and check out the Clusters by Parent Topic tab.
Then hit the Questions tab for pre-clustered, long-tail queries to target in your content…
To see how much ownership you have over existing long-tail query permutations, add a Target filter for your domain.
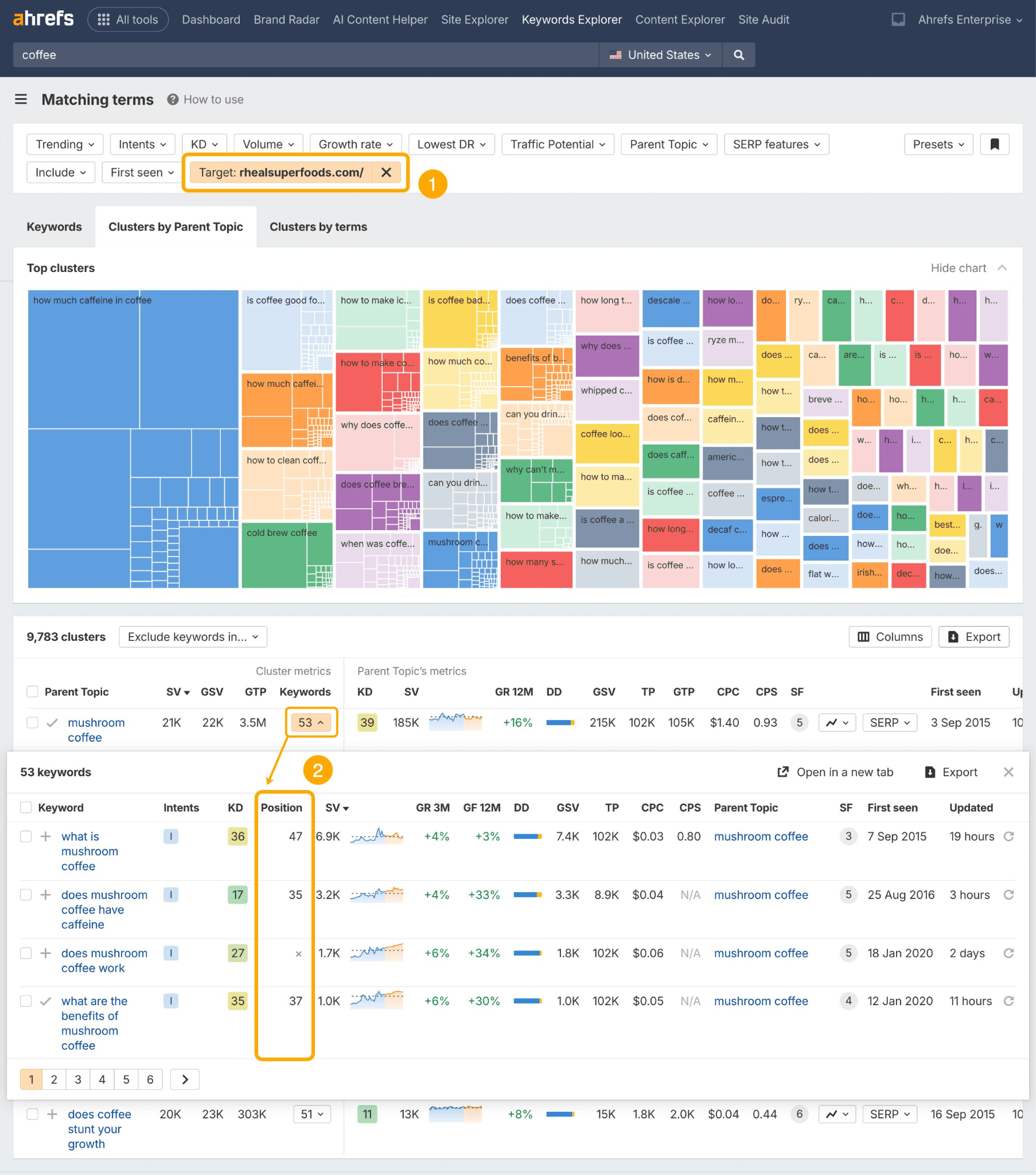
Content clusters aren’t new. But evidence points to them being of even greater importance in LLM search.
This suggests that a significant number of users are turning to AI for task completion.
In response, you may want to start action mapping: considering all the possible tasks your customers will want to complete that may in some way involve your brand or its products.
To map customer tasks, head to Ahrefs Competitor Analysis and set up a search to see where your competitors are visible–but you’re not.
Then filter by relevant action keywords (e.g. “make”, “track”, “create”, “generate”) and question keywords (e.g. “how to” or “how can” ).
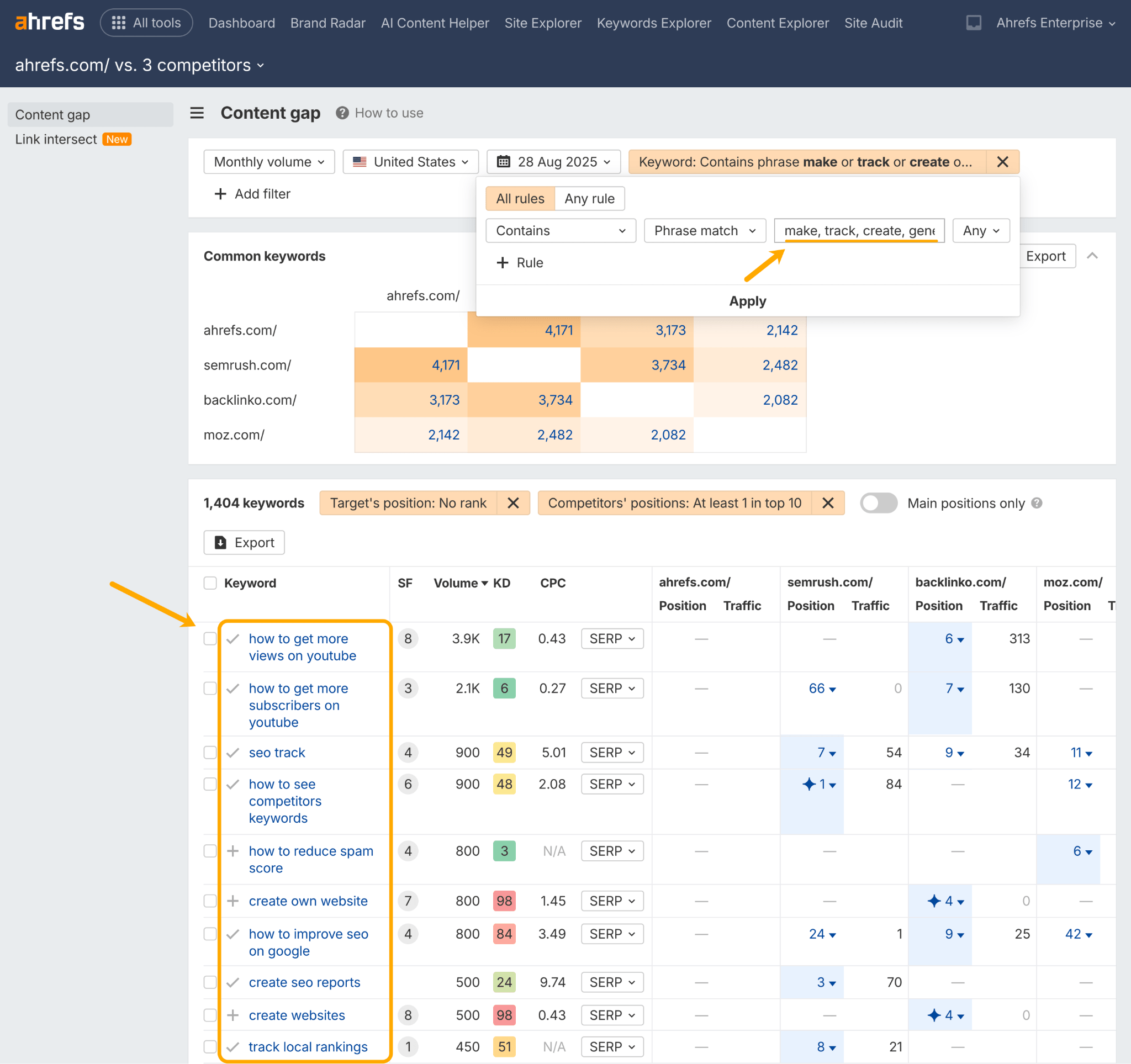
Once you know what core actions your audience wants to take, create content to support those jobs-to-be-done.
Content cited in AI is 25.7% fresher than content in organic SERPs, and AI assistants show a 13.1% preference for more recently updated content.
ChatGPT and Perplexity in particular prioritize newer pages, and tend to order their citations from newest to oldest.
Why does freshness matter so much? Because RAG (retrieval-augmented generation) usually kicks in when a query requires fresh information.
If the model already “knows” the answer from its training data, it doesn’t need to search.
But when it doesn’t—especially with emerging subjects—it looks for the most recent information available.
In the example below, Hubspot sees 1,135 new AI Overview mentions from a single content update, based on Ahrefs Site Explorer data.
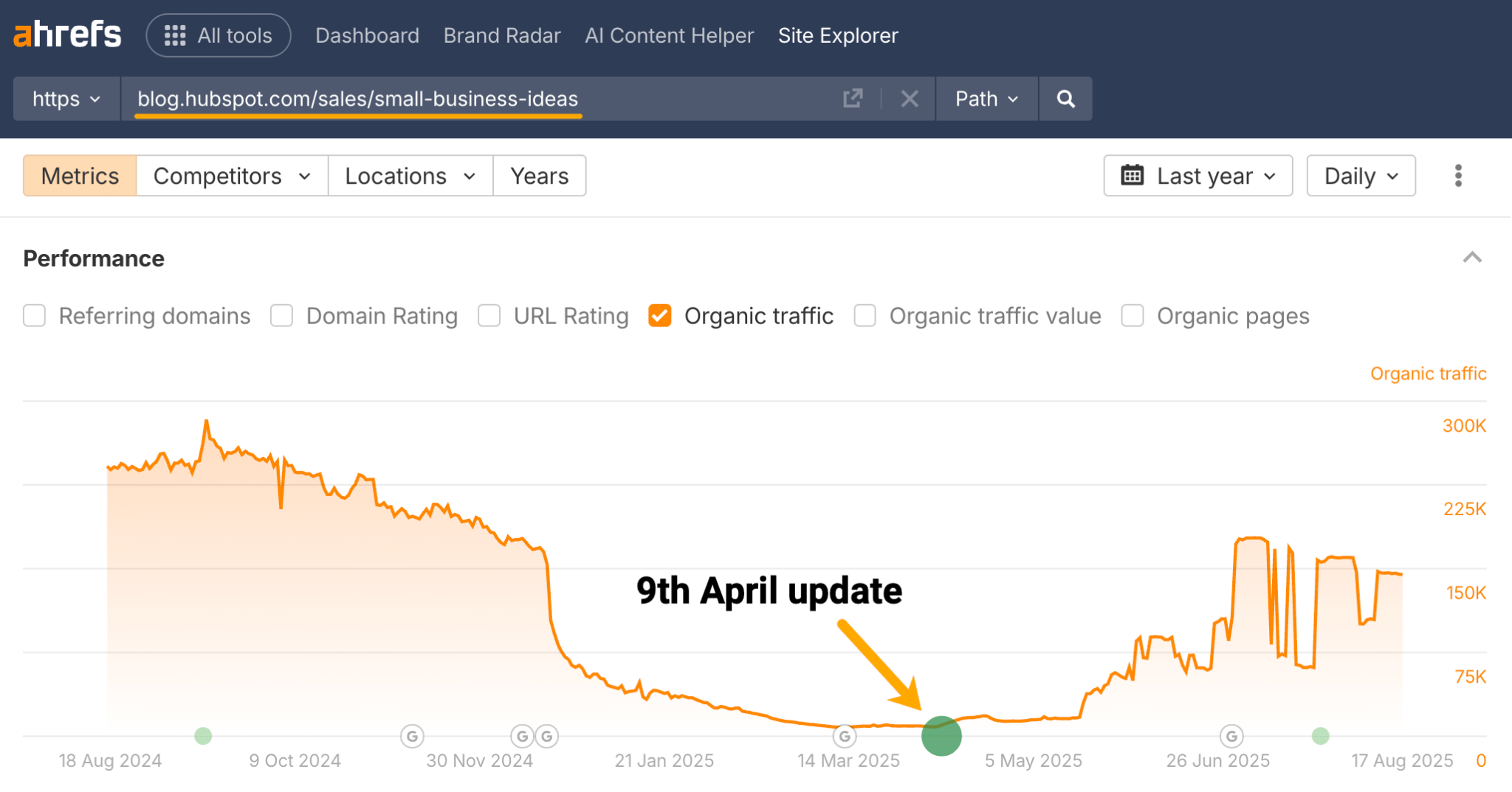
The article is now their most cited blog in AI Overviews, according to Ahrefs Brand Radar.
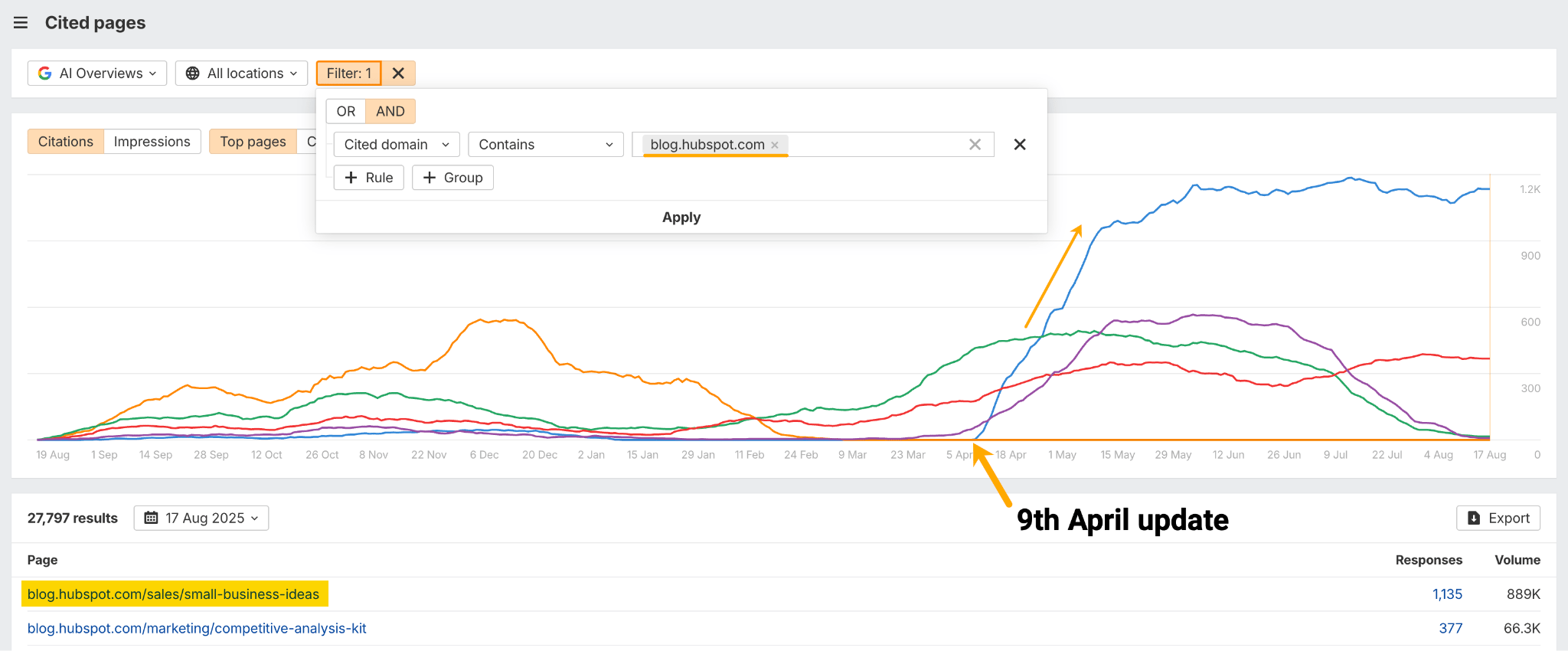
Our research suggests that keeping your content updated can increase its appeal to AI engines looking for the latest information.
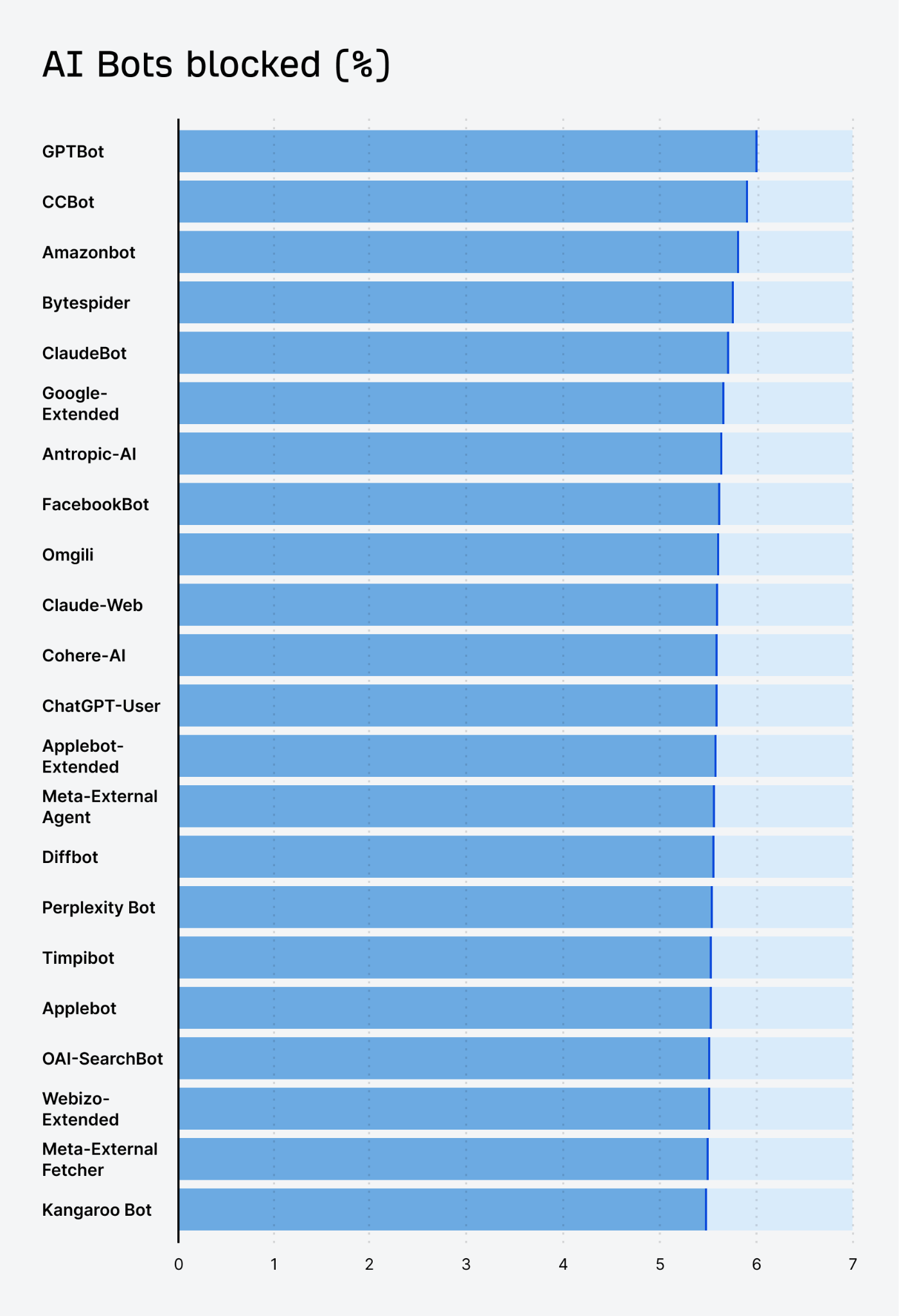
While that’s understandable, blocking might also mean forfeiting future AI visibility.
If your goal is to have ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini and other AI assistants mention your brand, double-check your robots.txt and firewall rules to make sure you’re not accidentally blocking major AI crawlers.
Make sure you let the legitimate bots index your pages.
This way, your content can be part of the training or live browsing data that AI assistants draw on—giving you a shot at being cited when relevant queries come up.
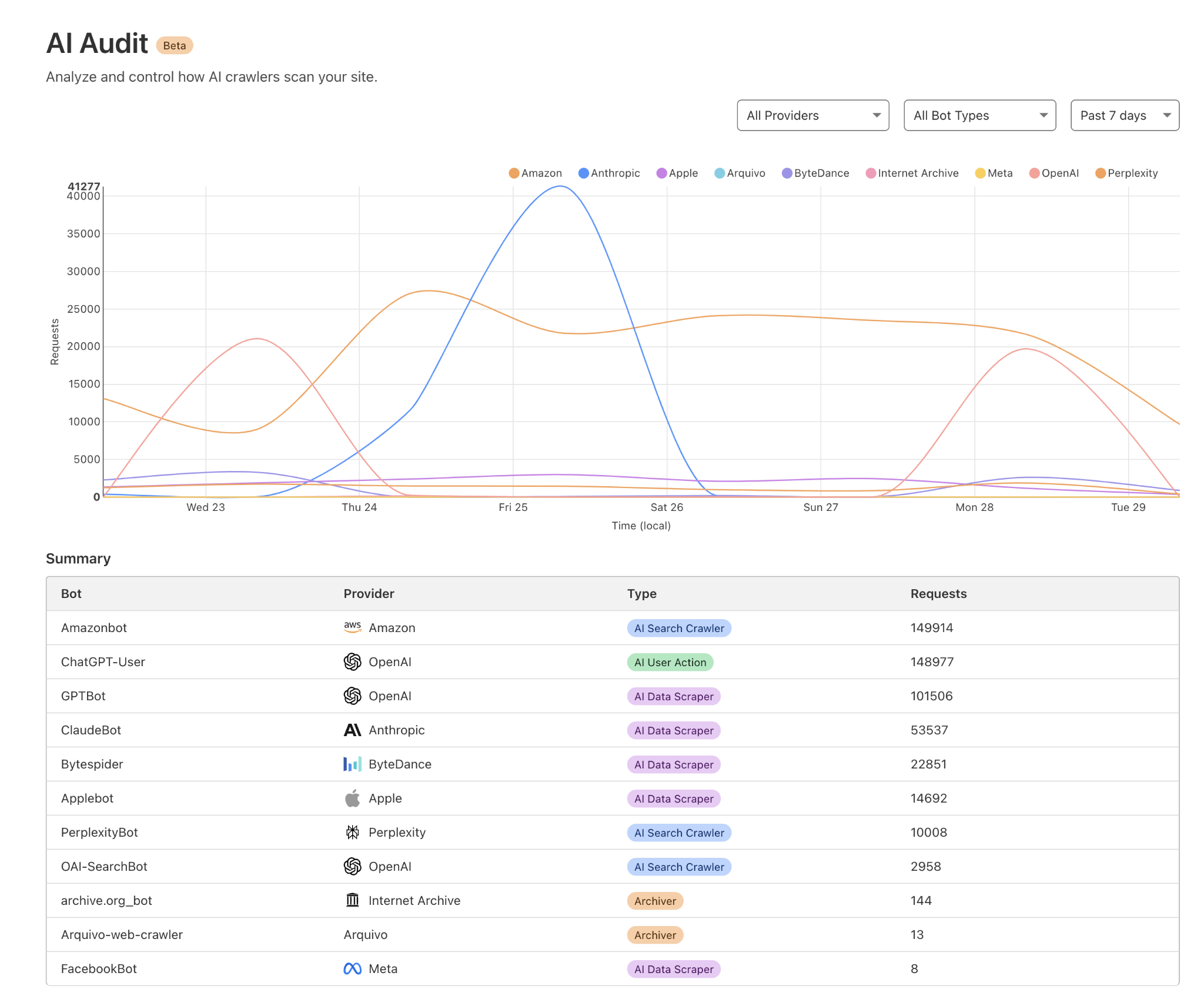
You can check which AI bots are accessing your site by checking your server logs, or using a tool like Cloudflare AI audit.
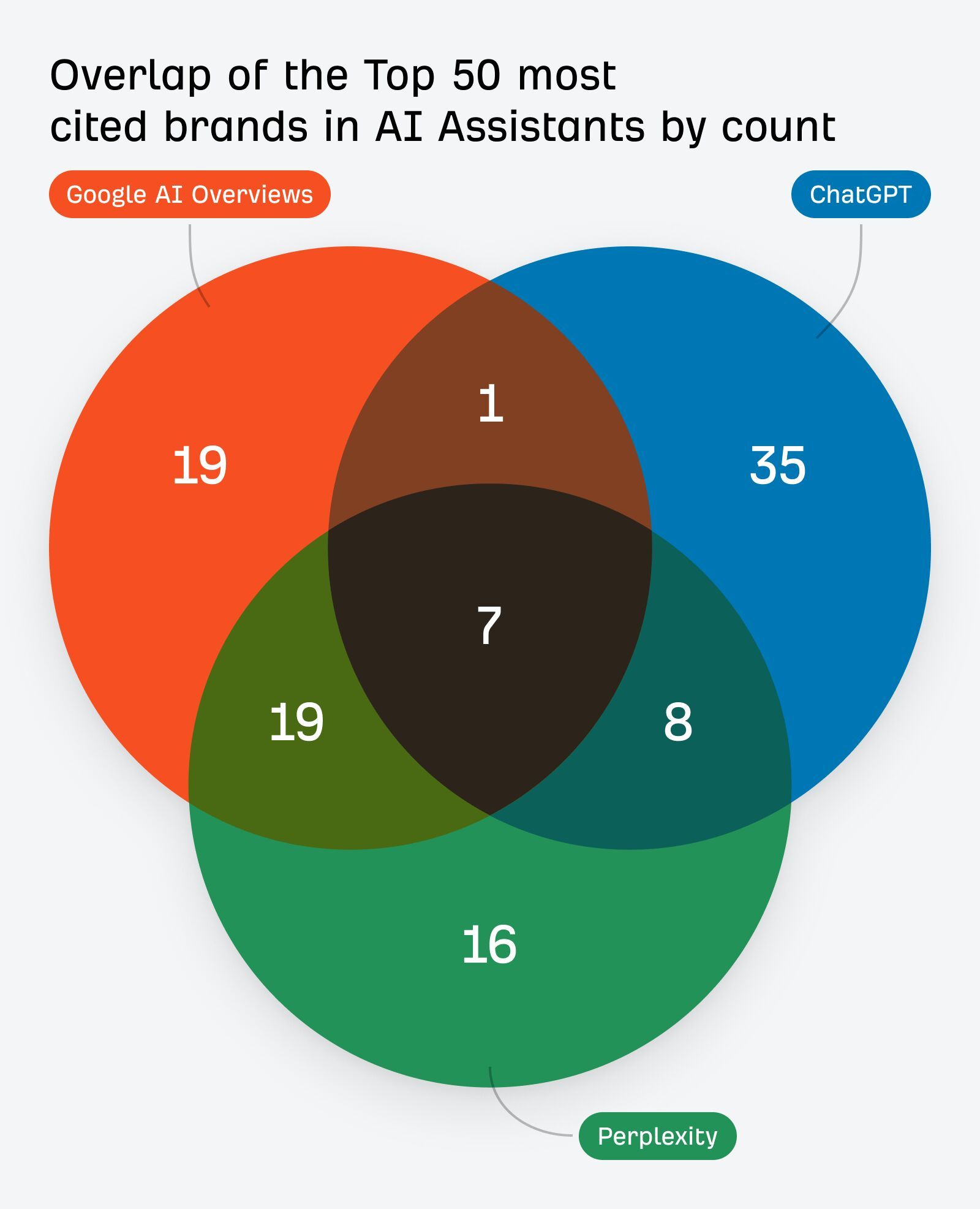
That means a staggering 86% of the sources were unique to each assistant.
Google leans on its own ecosystem (e.g. YouTube), plus user-generated content—especially communities like Reddit and Quora.
ChatGPT favors publishers and media partnerships—particularly news outlets like Reuters and AP—over Reddit or Quora.
And Perplexity prioritizes diverse sources, especially global and niche sites—e.g. health or region-specific sites like tuasaude or alodokter.
There’s no one-size-fits-all citation strategy. Each AI assistant surfaces content from different sites.
If you only optimize for Google rankings, you might dominate in AI Overviews but have less of a presence in ChatGPT.
On the flip side, if your brand is picked up in news/media it might show up in ChatGPT answers—even if its Google rankings lag.
In other words, it’s worth testing different strategies for different LLMs.
You can use Ahrefs to see how your brand appears across Perplexity, ChatGPT, Gemini, and Google’s AI search features.
Just plug your domain into Site Explorer and look at the top-level AI citation count in the Overview report.
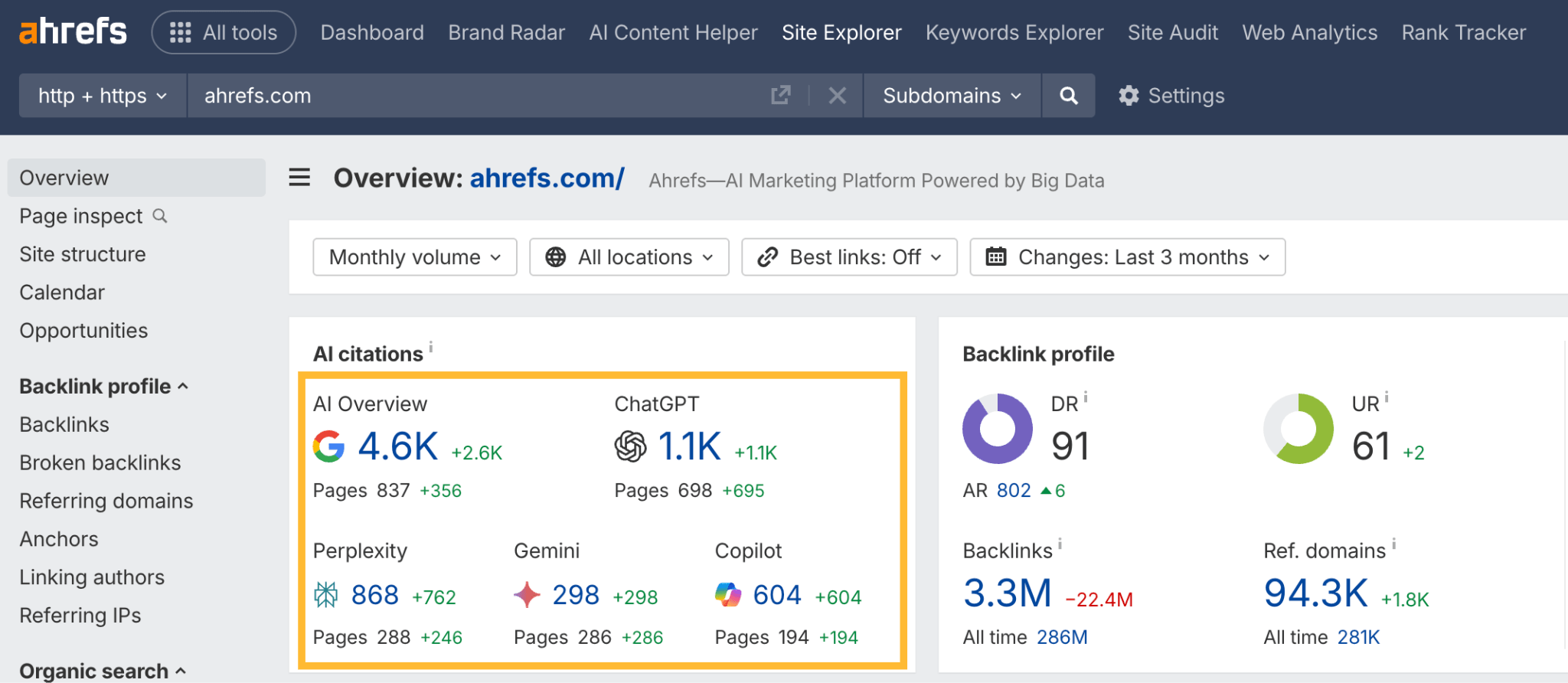
Then do a deeper dive in the Cited Pages report of Brand Radar.
This will help you study the different sites and content formats preferred by different AI assistants.
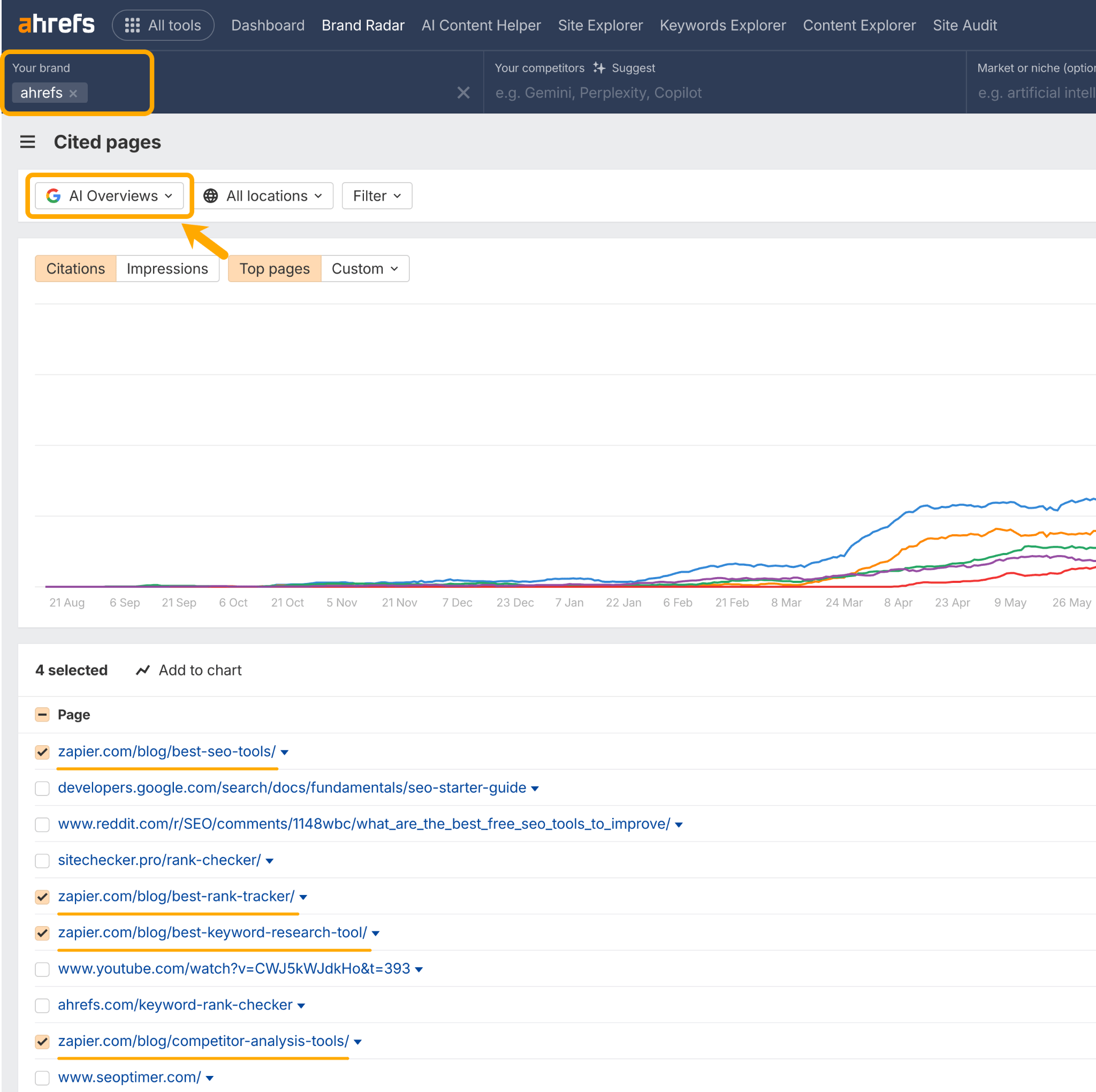
For example, mentions of Ahrefs in AI Overviews tend to pull from Zapier via “Best” tool lists.
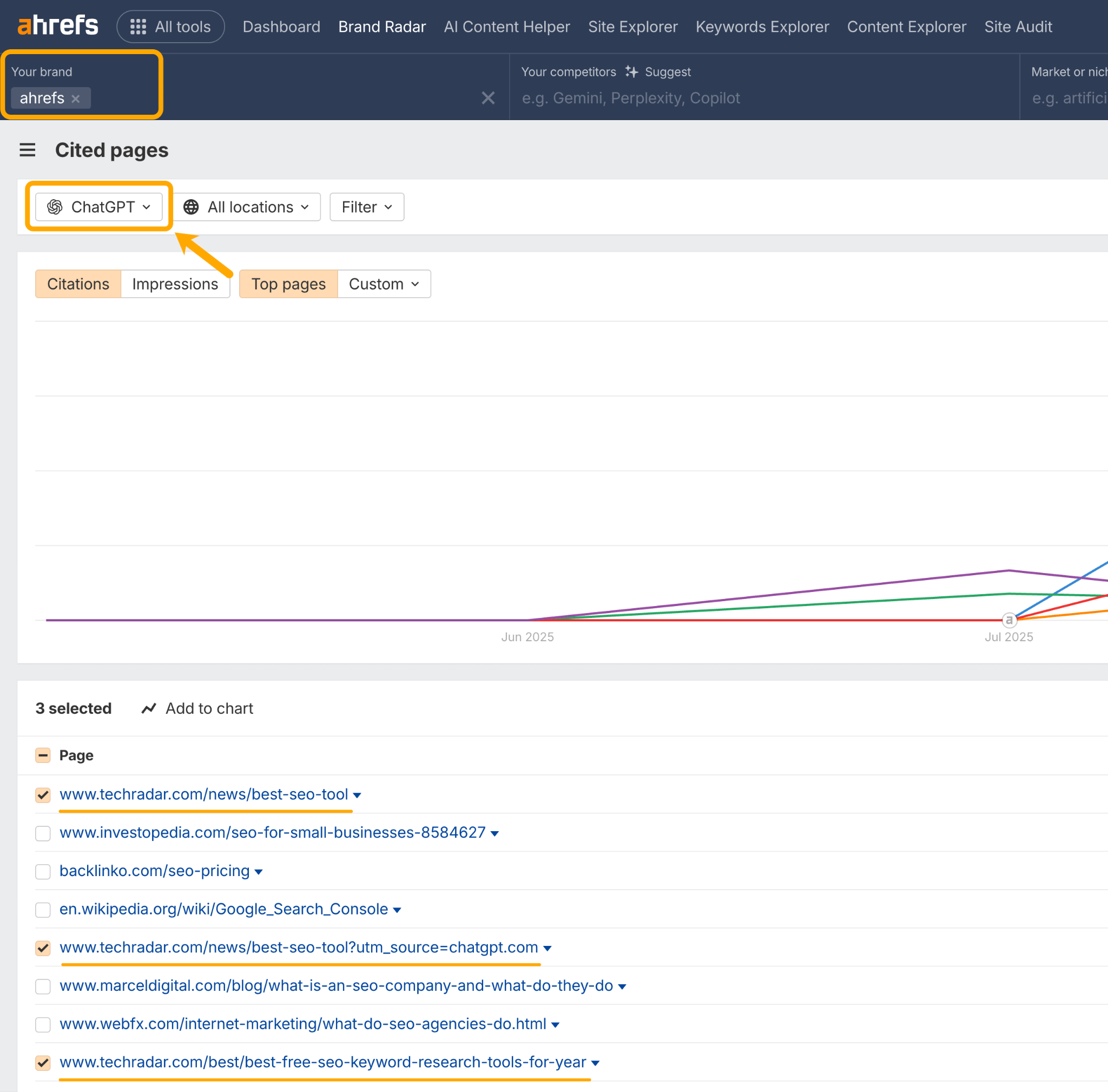
Whereas in ChatGPT, we’re mentioned more in Tech Radar “Best” tool lists.
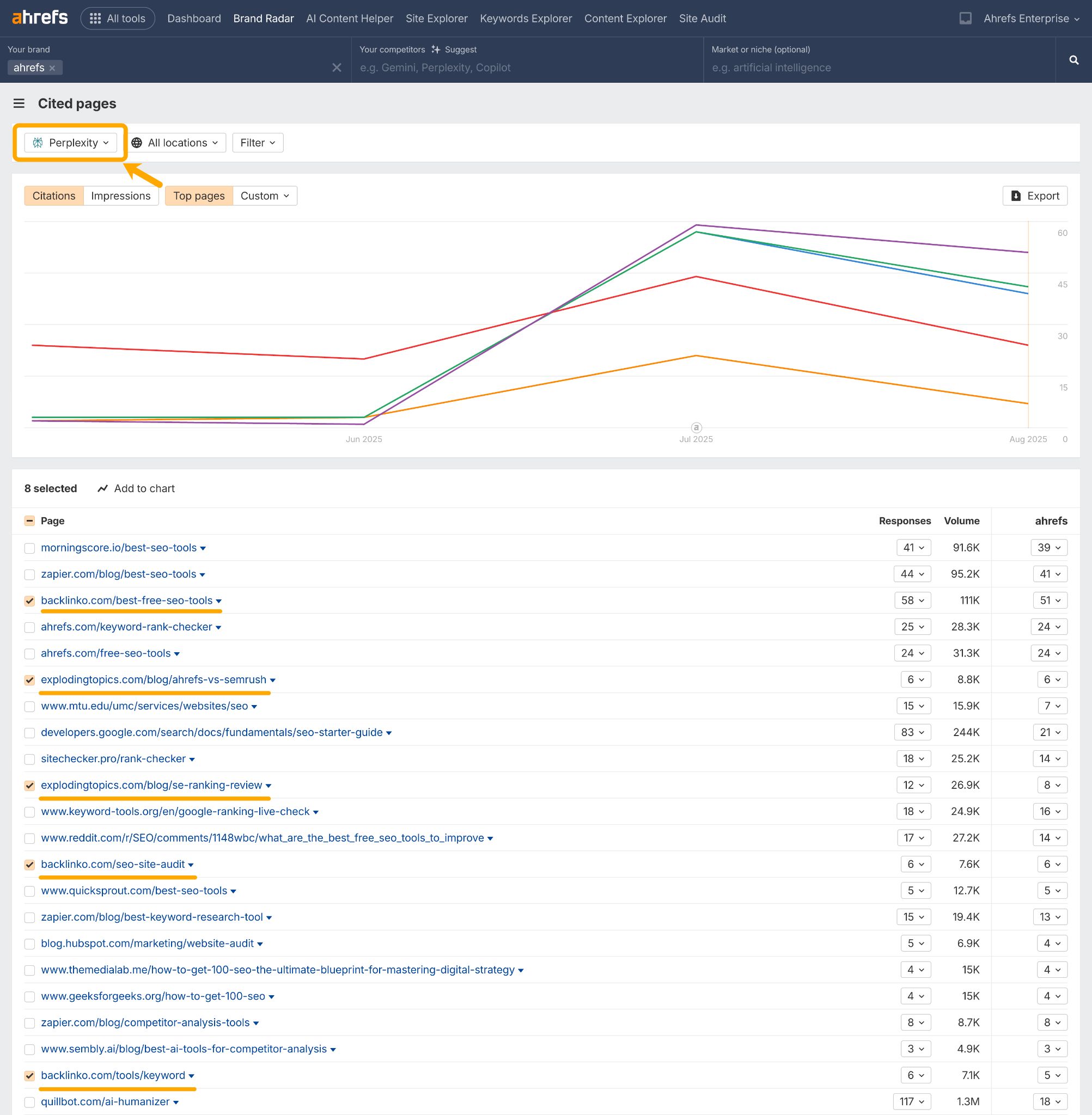
And in Perplexity our top competitors are controlling the narrative with “vs” content, “reviews”, and “tool” lists.
With this information, we can:
- Keep Zapier writers aware of our product developments, in hopes that we’ll continue being recommended in future tool guides, to drive AI Overview visibility.
- Ditto for Tech Radar, to earn consistent ChatGPT visibility.
- Create/optimize our own versions of the competitor content that’s being drawn into Perplexity, to take back control of that narrative.
Final thoughts
A lot of this advice may sound familiar—because it’s largely just SEO and brand marketing.
The same factors that drive SEO—authority, relevance, freshness, and accessibility—are also what make brands visible to AI assistants.
And tons of recent developments just prove it: ChatGPT has recently been outed for scraping Google’s search results, GPT-5 is leaning heavily on search rather than stored knowledge, and LLMs are buying up search engine link graph data to help weight and prioritize their responses.
By that measure, SEO is very much not dead—in fact it’s doing a lot of the heavy lifting.
So, the takeaway is: double down on proven SEO and brand-building practices if you also want AI visibility.
Generate high-quality brand mentions, create structured and relevant content, keep it fresh, and make sure it can be crawled.
As LLM search matures, we’re confident these core principles will keep you visible.
Similar Posts

What Is an MCP Server, and Why Should Marketers Care?
MCP (Model Context Protocol) connects your AI tools directly to your marketing stack—your CMS, analytics, CRM, social platforms, and more—through one standardized connection. This means you can ask: ‘Show me which blog posts lost traffic last month, what keywords they rank for in Ahrefs, and how many support tickets mentioned those topics in Intercom’—and get…
My Favorite Wayback Machine Alternatives
The internet never forgets… unless the page vanishes, the site goes offline, or the content quietly changes overnight. That’s where web archiving tools come in. They allow you to access saved versions of web pages, even if they get taken offline. The Wayback Machine is the best-known option, but it isn’t perfect—it’s slow, sometimes misses…
ChatGPT May Scrape Google, but the Results Don’t Match
We know that AI assistants like ChatGPT access search indices, like Google and Bing, to retrieve URLs for their response. But how, exactly? To find out, we’ve run a series of experiments looking at the relationship between the URLs cited by AI assistants, and the results found in Google when searching for the same topics….
Top Google Searches (January 2025)
Get the week’s best marketing content As of 2024, the most searched thing on Google is “youtube.” The next most popular searched words are “amazon,” “facebook,” “gmail,” “wordle,“and “google.” Below are lists of the top 100 most popular searches and questions in the US and worldwide, pulled from our database of 28.7 billion keywords: Keywords…
Answer Engine Optimization: How to Win in AI-Powered Search
Search is changing. People are no longer just “Googling it.” Increasingly, they’re asking AI systems for answers and getting them instantly without having to click and sift through different websites. SEO is still essential for brands to show up in these answers, but visibility now depends on more than rankings. What matters is whether your…

Short Domain Names: A Top Guide to the Benefits of Short URLs & How To Find Them
What can a short domain name do for your business? Are there even any left to choose from? Find out more. Short domain names can pack a punch, so it’s no wonder they’re so popular. Some of the biggest companies in the world use them and with good reason. In this article, we’re going to…