In 30 seconds, here’s what you need to know about the differences between SEO and GEO:
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization): Getting your website to show up in Google searches. Goal: Get people to click your link.
- GEO (Generative Engine Optimization): Getting AI chatbots like ChatGPT to mention your brand or information. Goal: Get AI to quote and mention you.
- Main differences: SEO brings visitors to your website. GEO puts your brand or content directly in AI answers (no click needed). SEO brings high-volume traffic that explores your site. GEO will bring less traffic to your site directly, but these visitors may be more likely to convert.
- What to do: Start with good SEO (it’s still essential), then add GEO tactics like including more original data, keeping your most important content up-to-date, or getting your brand mentioned more across the web.
- Bottom line: You need both. Think of SEO as your foundation and GEO as future-proofing your online presence.
Want the full story? Read on.
Further reading
In other words, GEO is SEO for AI search.
How AI search works
With ChatGPT, the way it responds depends on whether it uses web browsing (also called grounding) to find the answer:
- No browsing: It generates answers from patterns it learned during training. It doesn’t pull from a live product database, just from its frozen knowledge (up to August 2023).
- With browsing: It searches the web, picks useful pages, and summarizes them so the answer is based on fresh information.
Key GEO tactics
All of these are covered in detail in our GEO guide, but here’s the quick version:
- Third-party mentions: Get your brand mentioned across industry sites, “best of” lists, and review platforms (most AI citations come from other sites, not yours).
- AI-preferred content: Create how-to guides, comparison pages (“X vs Y”), data studies, and “best of” lists – these get the highest AI traffic.
- Facts and statistics: Include specific, verifiable numbers and data that AI can confidently cite.
- Multi-platform presence: Build visibility on YouTube (2nd most cited by AI Overviews) and Reddit (3rd most cited).
- Structured Information: Use clear headings, Q&A formats, bullet points, and schema markup for machine readability.
- Fresh content: Keep information updated regularly – AI prefers citing newer content over older pages.
Further reading
They found that users click on search results only 8% of the time when AI summaries appear vs 15% without them – that’s nearly 50% fewer clicks. Only 1% of users click on sources cited in the AI summary itself. What’s more, 26% of users end their session completely after seeing an AI summary (vs 16% for traditional search).
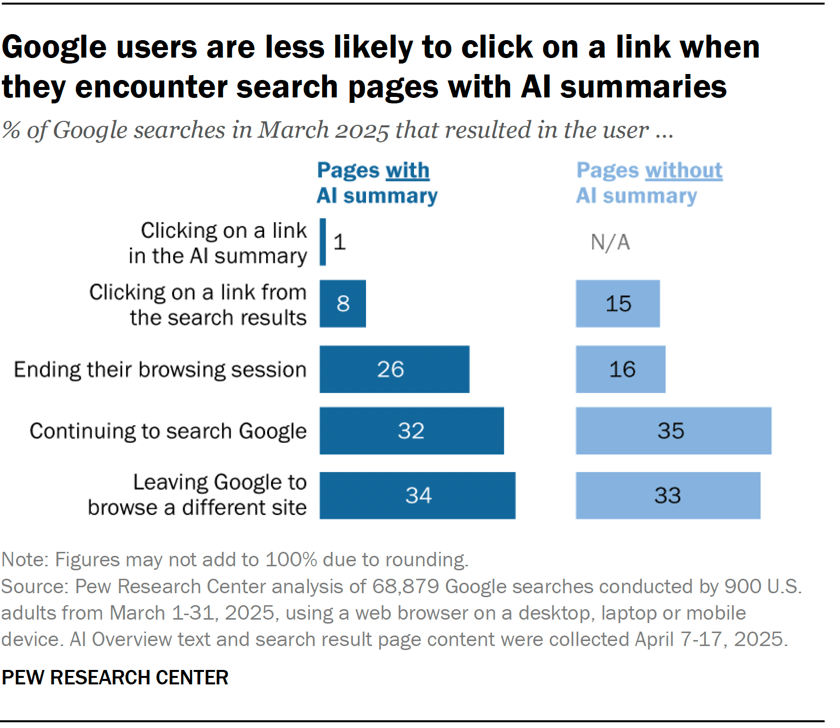
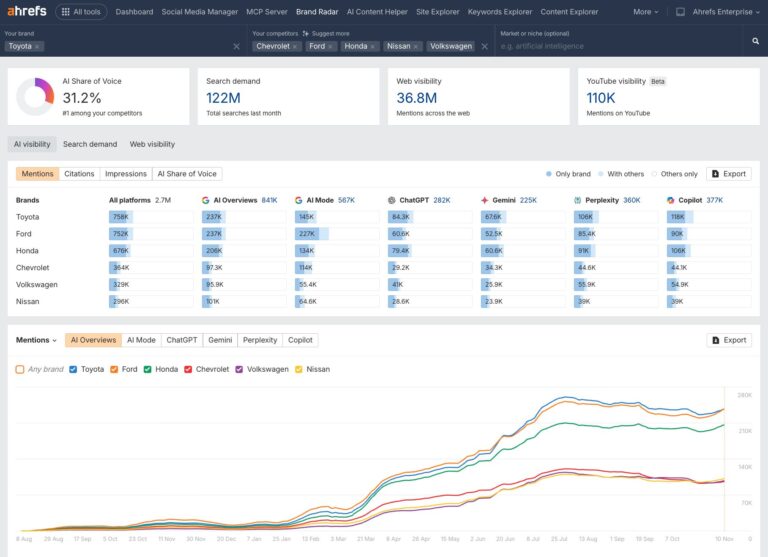
By contrast, success in GEO is measured with metrics like brand mentions in AI answers, citations when your content is referenced, AI referral traffic, and AI share of voice. This is “visibility economics,” where the more often your brand appears in AI responses, the more likely users are to trust and choose you, even if they never click.
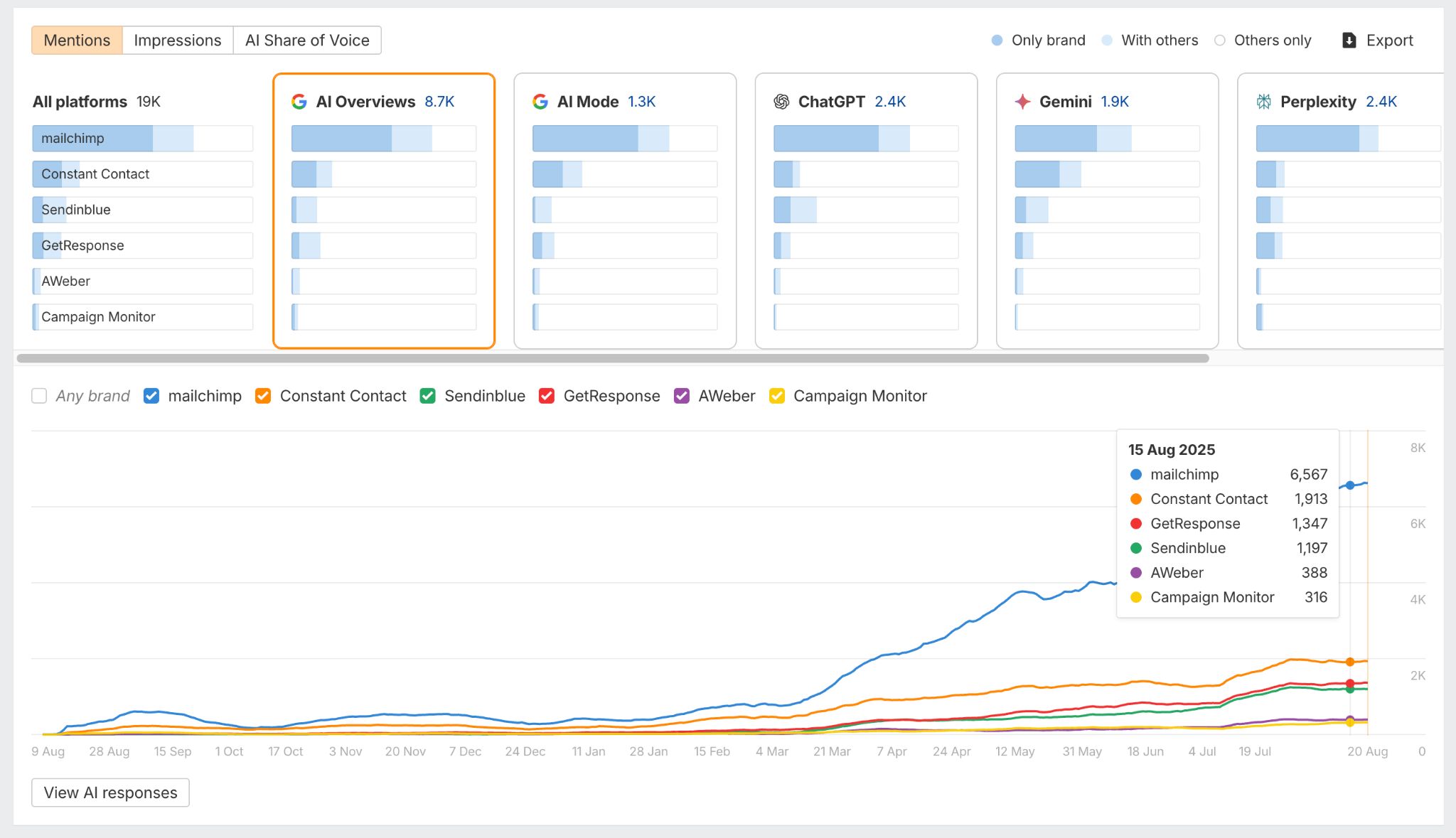
Here’s what a GEO dashboard looks like, a screenshot from Ahrefs’ Brand Radar. The core difference is that there are no keyword rankings. Instead, you see how popular a brand is within a specific AI’s responses, and how that popularity changes over time.
Further reading
AI search also drives users to homepages, product pages, and tools more often than organic search, while organic search brings more traffic to international pages.
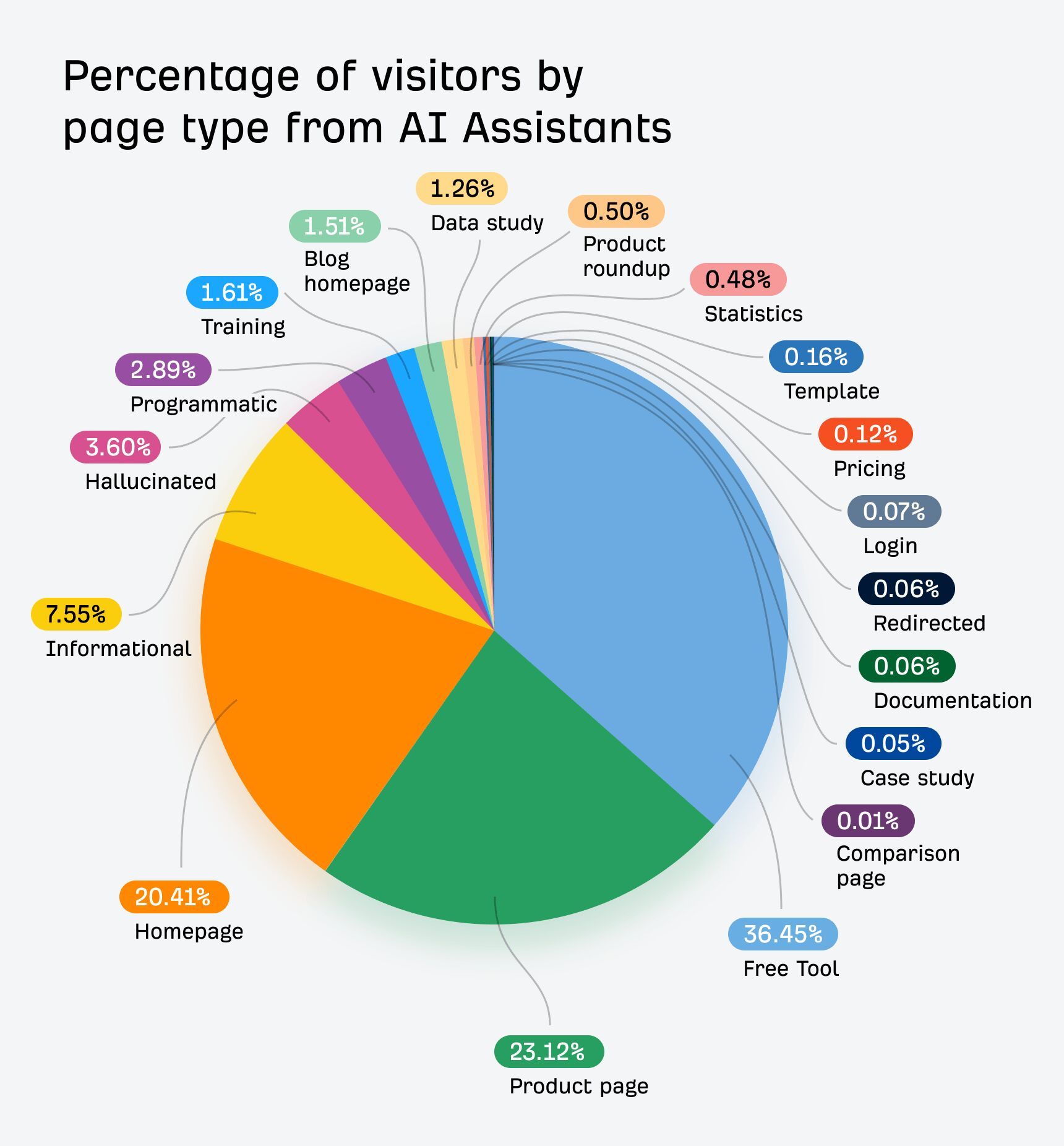
Most importantly, AI traffic can convert at a much higher rate. In the case of Ahrefs, it was 23x more than organic search; despite being just 0.5% of traffic, it generates over 12% of signups.
That said, conversion rates will vary by site. As this recent study from Amsive shows, not every website sees the same uplift from LLM-driven traffic.
Further reading
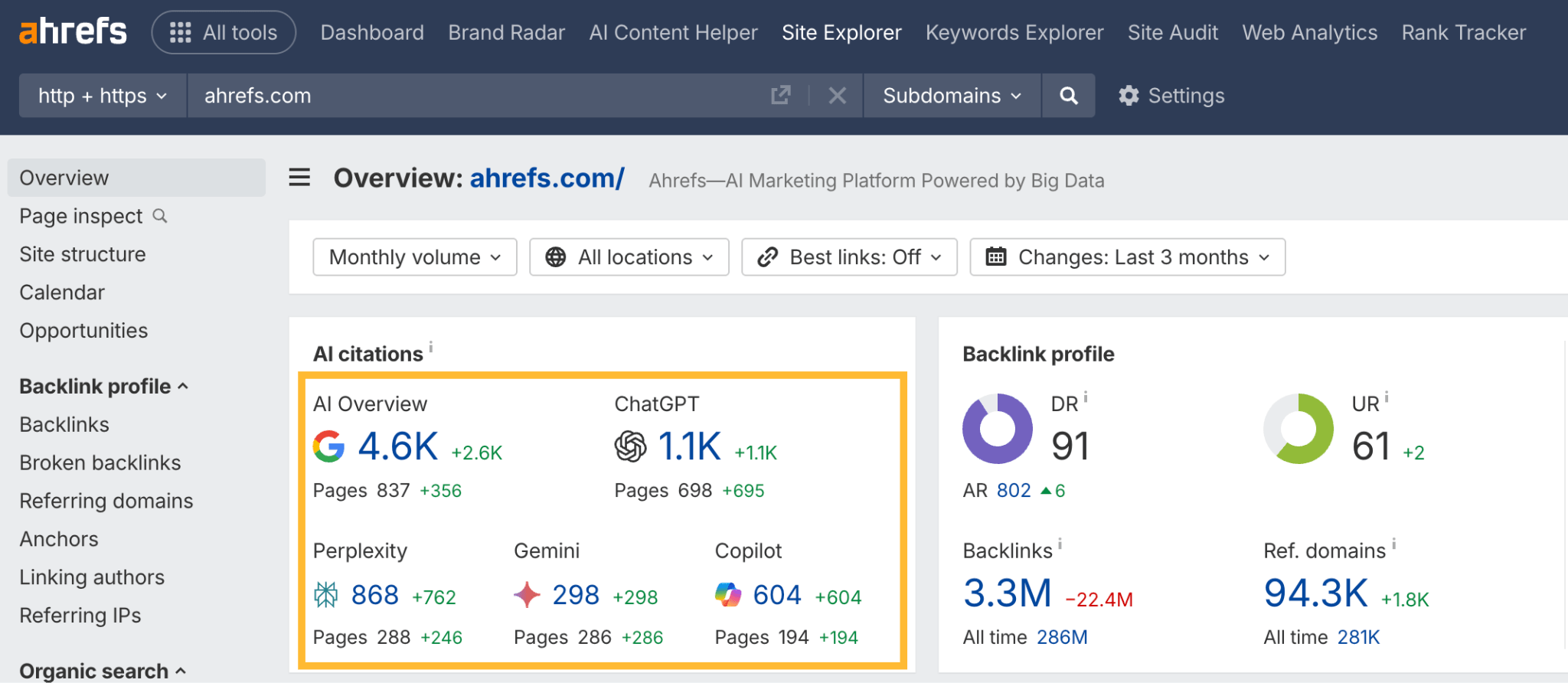
Case in point, Ahrefs’ content and product pages were mentioned 7,470 times across 2,309 pages without any special effort to optimize for AI. That’s because new search technologies still rely on the same foundation: quality, useful content.
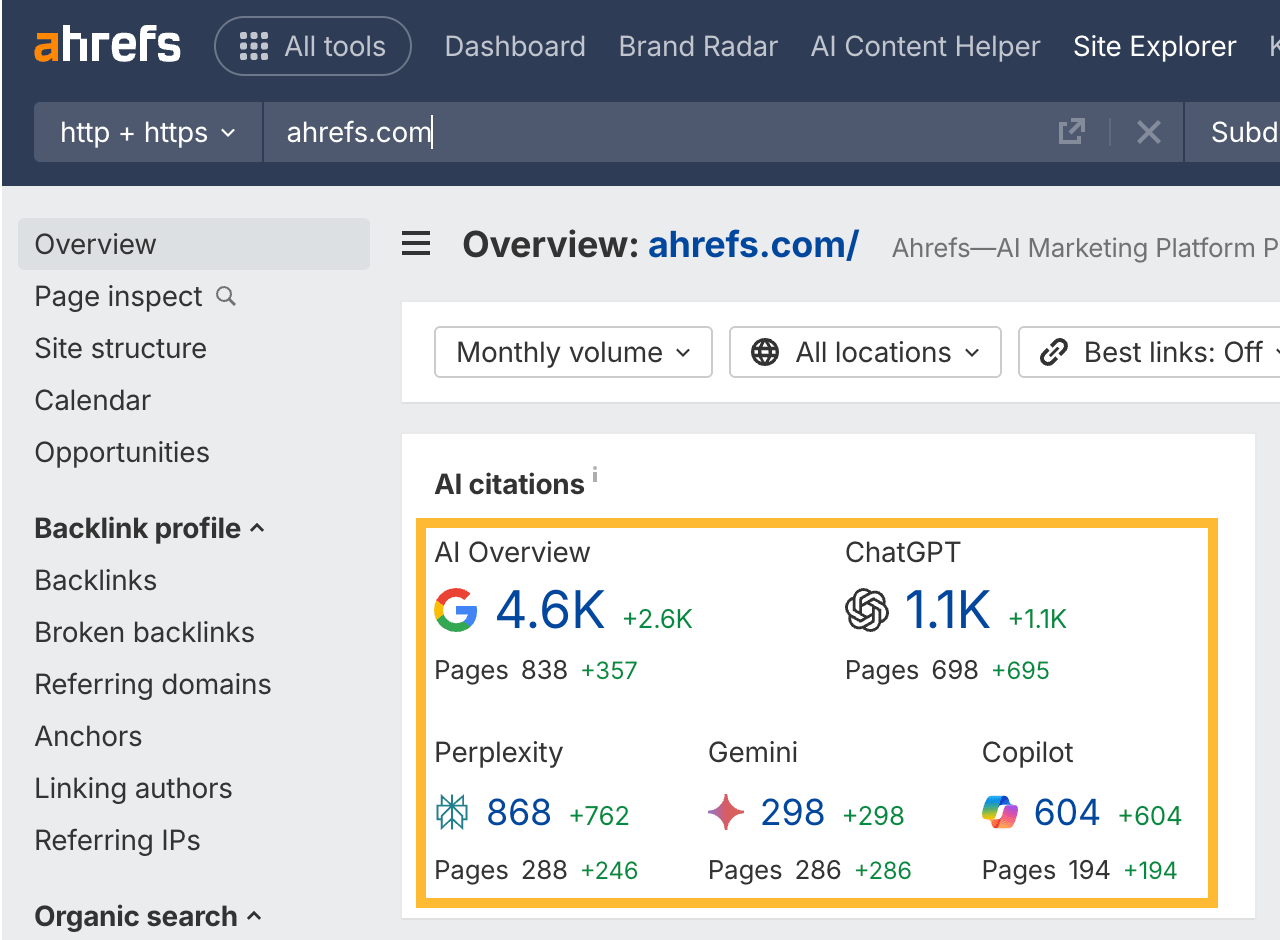
Whether someone searches Google for “best project management software” or asks ChatGPT something more specific like “What’s the best project management tool for a team of 30 under $50?”, the intent doesn’t change. They’re looking for the top options, the reasons behind those recommendations, and a clear comparison to help them decide.
Tip
Use Ahrefs’ AI Content Helper to take the guesswork out of content planning. Find the main topics (not just keywords) for your keyword by analyzing top-ranking pages. As you write, see your content rated in real time and adjust instantly.
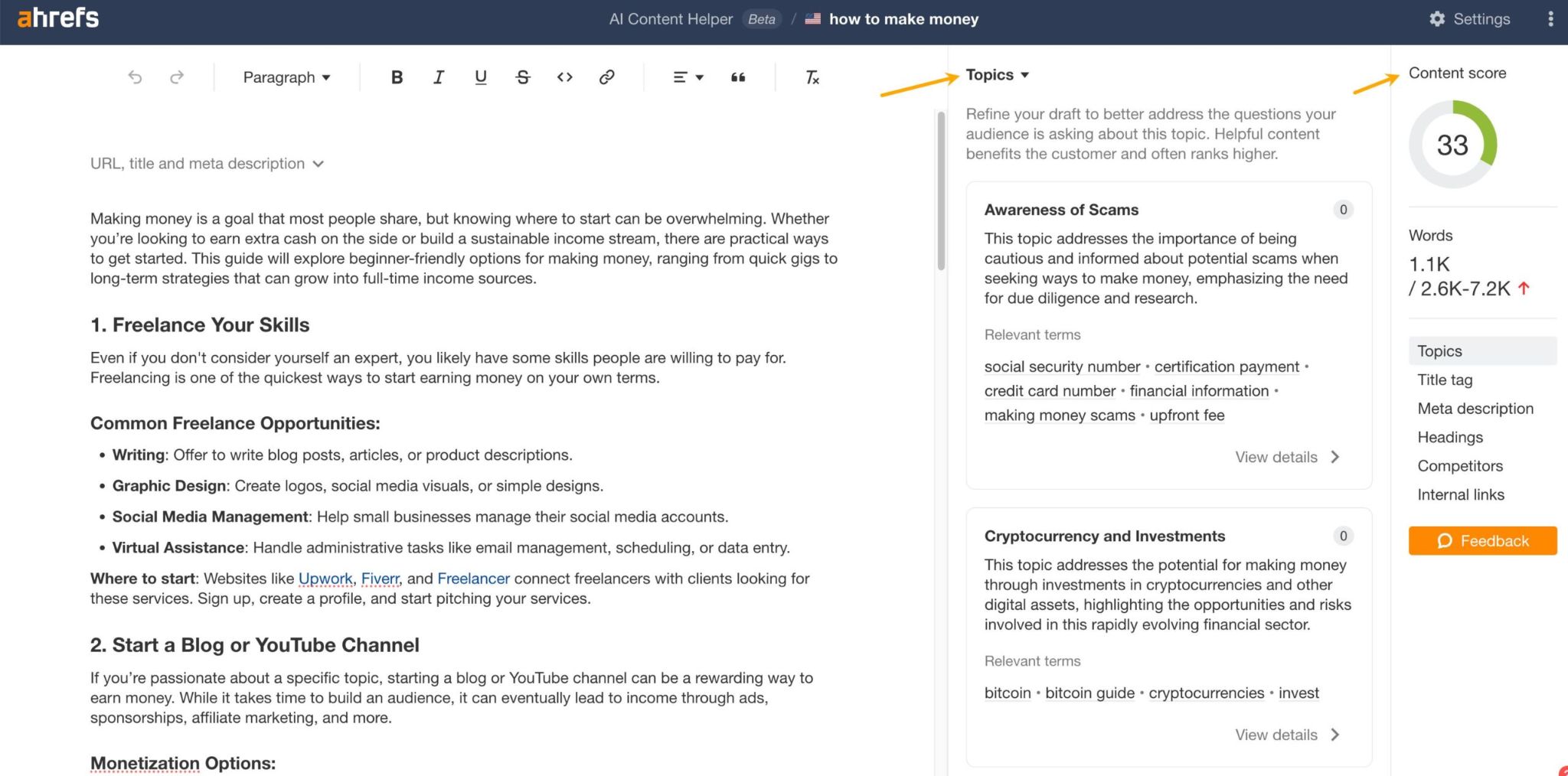
Create new articles or update old ones with ease. When search results mix different intents, simply pick the intent you want to optimize for and let the tool guide you.
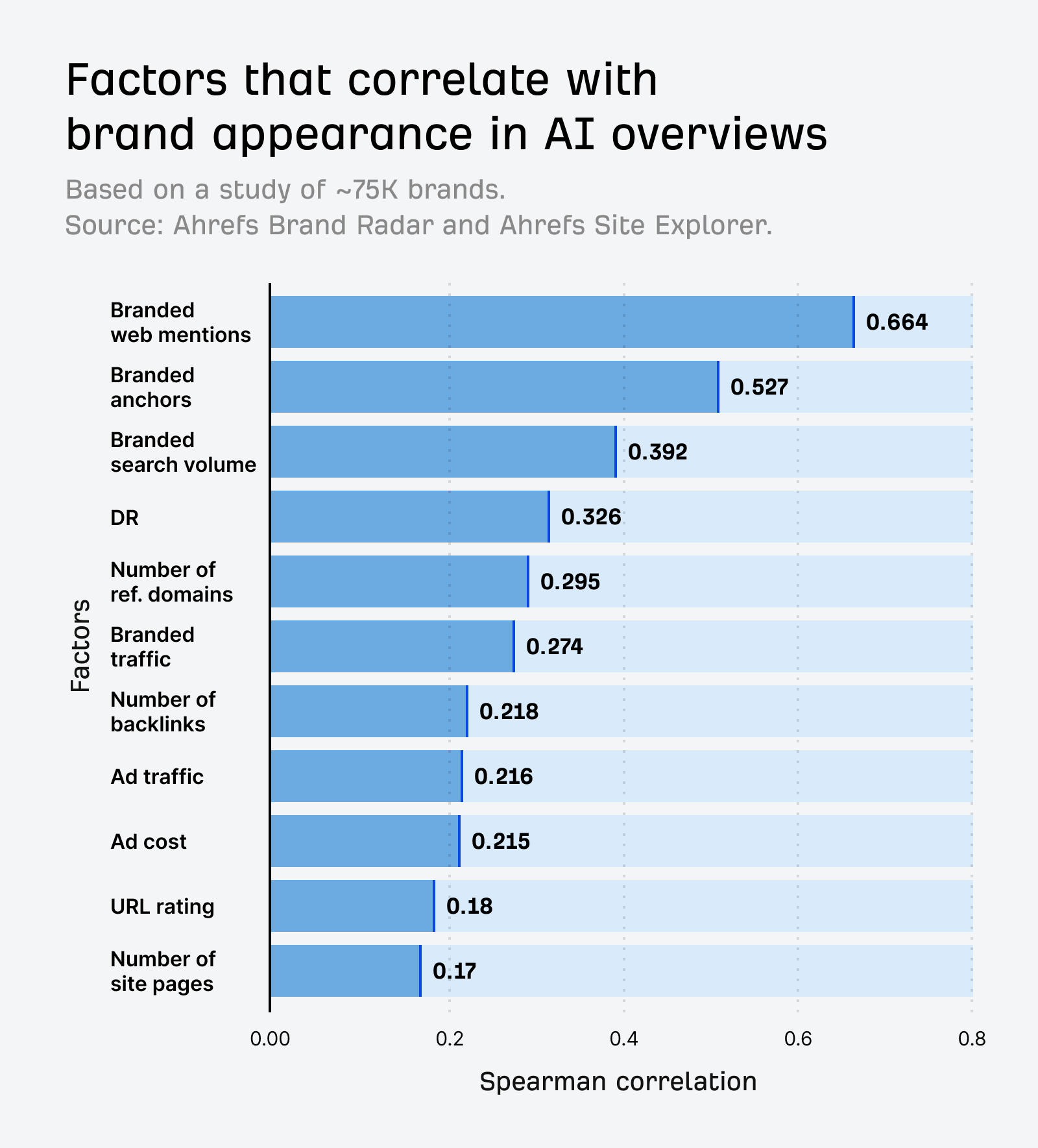
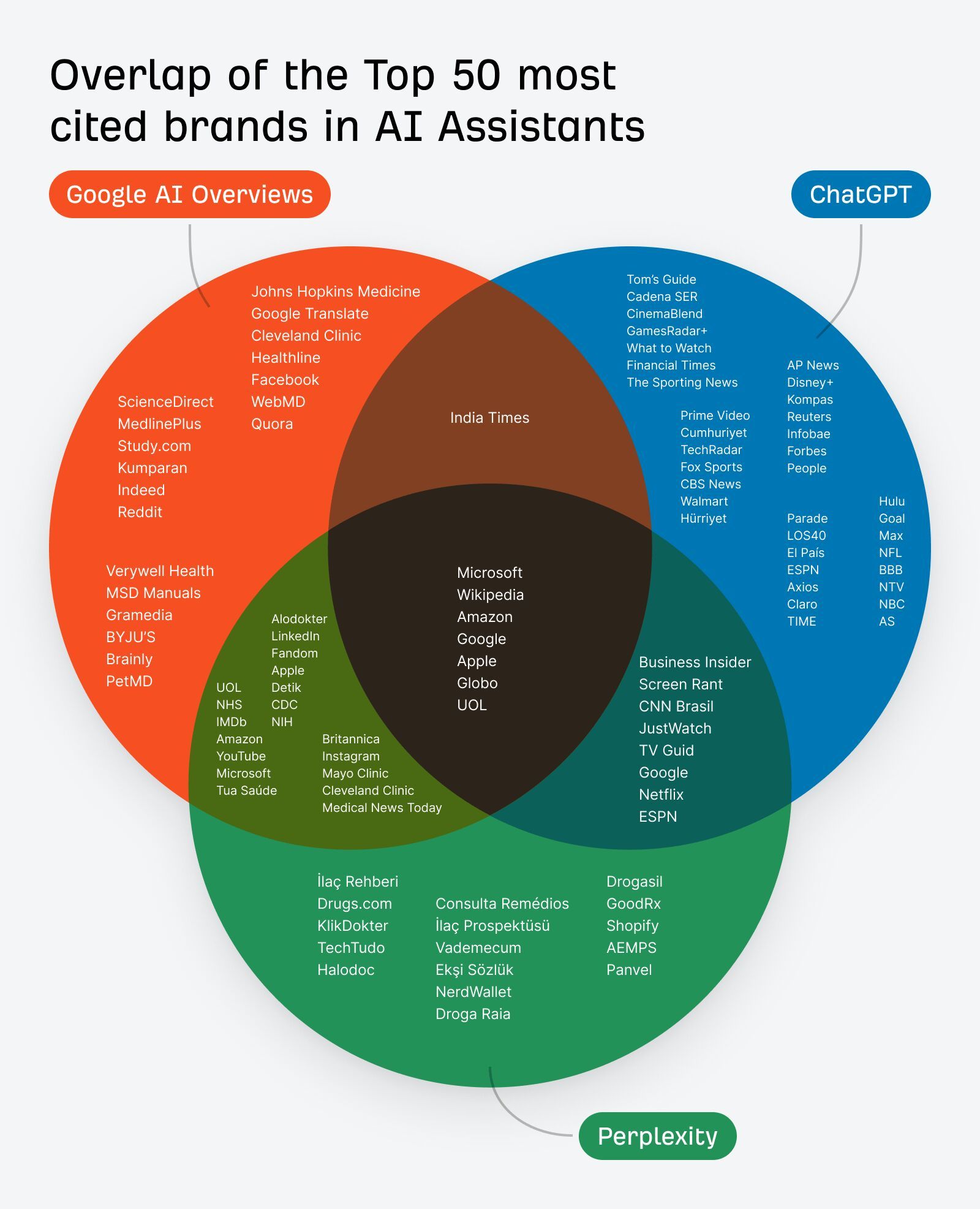
And that’s not just true for AI Overviews. AI Assistants also lean heavily on well-known sources. The main difference is that they tend to cite a slightly different set of sites.
Simply put, the more people talk about your brand online, the more likely AI is to feature you.
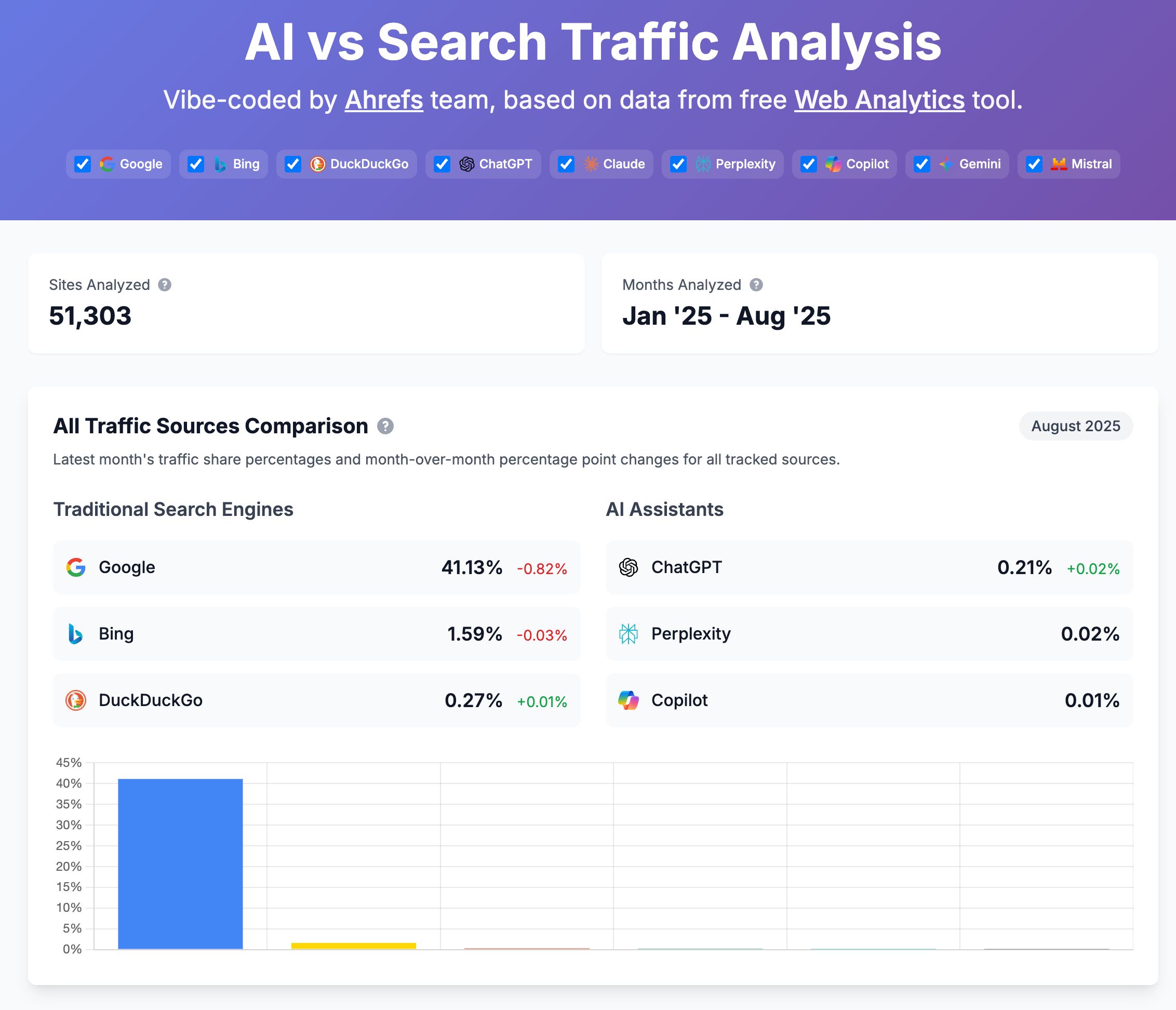
If you’re curious about the global traffic shift, check out our AI vs. Search Traffic Analysis dashboard, which pulls data from over 50,000 sites. For instance, from January to August 2025, Google held a 41.13% traffic share, while ChatGPT accounted for 0.21%.
Similar Posts
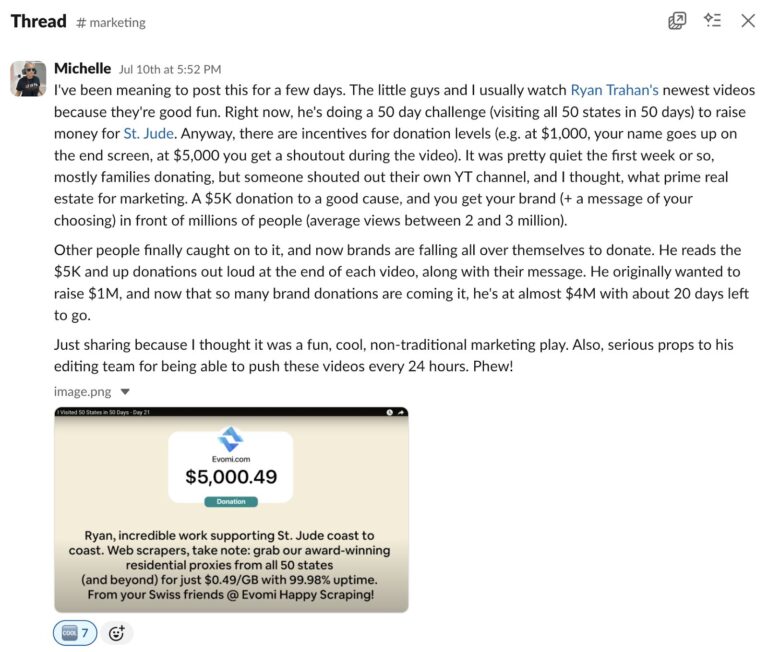
The Genius Marketing Strategy in Ryan Trahan’s 50 States Challenge
It started with a $100,000 donation, ended with $11 million raised for charity, and somewhere along the way, an electric bike brand earned 235M+ impressions and $7M worth of brand awareness. Ahrefs’ Community Manager, Michelle Lindner, shared Ryan Trahan’s “50 States Challenge” in our #Marketing Slack channel after watching it with her kids. She thought…
How to Monitor and Win Brand Mentions in AI Answers
Brand mentions happen when people talk about your company online without necessarily linking to your website. They’ve always happened on social media, forums, news sites, and blogs. But now they’re happening in AI responses—and these mentions influence how millions of people discover and perceive your brand. Welcome to the new era of brand mention monitoring. ChatGPT,…
I Reviewed the Best AI Search Engines for 2025
I rigorously tested the most popular AI search engines to discover their strengths and weaknesses. I ran this test for two reasons: As a human being, I want to use the best search engine around. I spend my life on the internet. I want to find information in the fastest, most effortless way possible. As…
AI Overviews Change Every 2 Days (But Never Change Their Mind)
Just how stable are AI Overviews? If you manage to get your brand mentioned or cited in them, can you take the rest of the month off? Or do you have to fight for ongoing visibility? To find the answers, our data scientist, Xibeijia Guan, analyzed over 43,000 keywords—each with at least 16 recorded AI…
Republishing Content for SEO & AI: How to Update Posts (Not Just Change Dates)
But updating website content shouldn’t just mean changing a publish date. It’s a chance to improve user experience, build your owned audience, and shape how AI represents your brand. I’ll walk you through tactics that help you accomplish all of the above—without eating up days of your time. Watch tutorial on YouTube keyword research and written great content, it’s…

17 Proven SaaS Marketing Strategies From 11 CMOs & Founders
Over the past year, we interviewed top SaaS founders and marketing executives on the Ahrefs Podcast. We asked them about strategies that helped them scale. From Crypto.com to Airwallex, Paddle, and Surfer, these battle-tested methods have fueled growth in competitive markets with limited resources. In this article, we share their best insights so you can apply…
